You may be wondering what flywheel is. In the literature on the subject, it's also known as flywheel marketing.
It's about a new approach to the classic sales funnel model. It's about changing the mindset from linear to circular.
What's all the fuss about? Why is it worth familiarizing yourself with the flywheel model? Is this a change in thinking on the scale of Copernicus or a common buzzword, one of many in marketing and the intersection of marketing and user experience design?
How can the flywheel concept be used in user-centered design (UCD)?
Will this new approach be useful for UX/UI designers in their daily work?
Okay, that's enough questions. We'll deal with the details in this article. We'll think and figure things out. We can do it!
As always, we cordially invite you to read on!
What is the flywheel sales model?
At first glance, the difference between these models—sales funnel and sales flywheel—doesn't seem spectacular. It doesn't seem significant or have much of an impact. It's true, but it doesn't have to make a huge impression. It's enough that the changes they cause are more striking.
Although maybe it's better to say in a more cautious and balanced tone that it is a model that is simply more relevant for today's market and technological realities. It fits better with the new standards, trends, and changes.
We can't help but notice that the change in thinking about the movement of planets and the sun also didn't sound particularly complicated because it didn't have to. All that's important is that it resulted in changes in the social and political worlds. It simply changed the course of history.
Will that also be the case with the flywheel? It's hard to say, but the change in thinking and approach will undoubtedly open many new possibilities and chances.

This is because it can be intensified with tools, approaches, research, and standards that have been used for a long time in UI/UX design.
In theory and practice, this matter is quite simple. All it takes is to combine the flywheel model with the body of knowledge, experiences, and methods used in user experience.
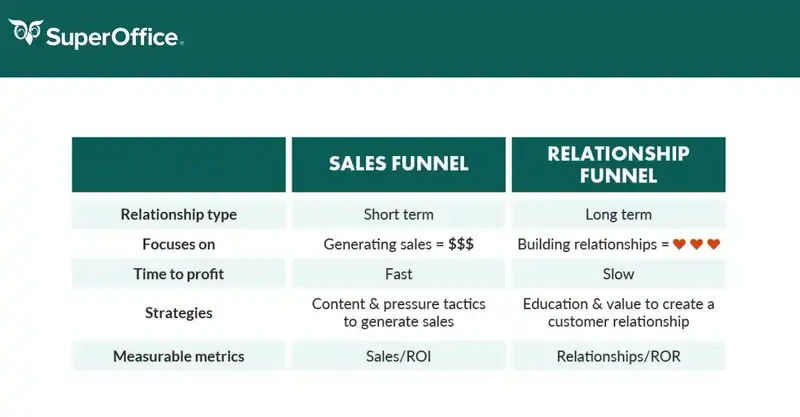
Okay, a theory is a theory, but what about the details? Let's start with the definition of key terms. What is a sales funnel, also known as a customer funnel, marketing funnel, or conversion funnel?
Regardless of your preferred name, the funnel is a tool used by sales and marketing teams. It's a graphical representation of the process, the potential customer journey in which the first contact with a brand, product, or company is the beginning, and the purchase of a product or use of a service is the end.
The funnel metaphor is not coincidental.
Widest at the top and gradually narrowing towards the bottom — the funnel — it's a good visual representation of how a significant number of potential customers shrinks over time to become a small group of viable customers.
The sales funnel model distinguishes various stages, and this conceptualization of the process allows you to understand better its conditions, dynamics, limitations, and possibilities.
The ultimate goal of using the funnel model is to improve conversion, increase sales, and discover moments when the company loses the interest of its potential customers.
That said, the sales funnel model consists of 4 stages:
- Awareness
- Interest
- Desire
- Action
Even if you aren't a marketing guru, we're sure that the funnel model seems familiar to you. Yes. It's the modified version of the AIDA model (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action), which has been a fundamental marketing tool for decades.
Although it was considered canonical for many years, today, the sales funnel model is increasingly more often seen as archaic and less effective than one may want it to be.
The main argument against it is an excessive focus on attracting the attention of as many potential customers as possible while neglecting already existing customers.
The sales funnel is also used to analyze the effectiveness of online marketing activities.
The version of the sales funnel adapted to the needs of digital products contains three key stages:
- ToFu (Top of the Funnel) is the beginning of the funnel, in which the customer's awareness is awakened.
- MoFu (Middle of the Funnel) helps to understand the customer's condition and initial interest in the purchase.
- BoFu (Bottom of the Funnel) focuses on understanding and supporting purchasing decisions, increasing the conversion rate and sales volume.
As you can see, the concept of the sales funnel model is heavily focused on hard sales results.
It says little, almost nothing, about relationships, needs, and reactions. It operates with simple indicators of success — purchase or lack of it.
What are the main advantages and limitations of the sales funnel?
Advantages? Of course, if this model didn't have any, it wouldn't have been used on such a scale and with such conviction.
The sales funnel primarily gives structure and purpose to the processes of sales and acquiring customers and helps with using adequate for a given stage, methods to measure and optimize activities.
Moreover, the sales funnel allows you to reach specific customer groups precisely and effectively. It distinguishes and ranks groups within them.
It's also helpful when you want to discover the reasons behind abandoning a purchase. The sales funnel is invaluable as a method for selecting sales techniques.
However, nobody would want to change it for the new flywheel model if it didn't have clear limitations and annoying disadvantages. The sales funnel is a tool, method, and concept characterized by a significant narrowing of perspective.
It focuses on results and ignores causes, emotions, effects, and outcomes.
Absolutizes sales and disregards the relationship's potential with the customer, who cannot only repeat the purchase but also effectively persuade other customers to buy.
The sales funnel absolutizes the result and ignores the product's usefulness, satisfaction, and fulfillment guarantee. This model completely overlooks the purely human view.
Such a narrow-minded approach doesn't help build lasting customer relationships; it only results in a one-time purchase.

Consequently, it's not surprising that in the era of customer, user, and experience supremacy, it has been replaced, or soon will be, by a model that prioritizes complex customer needs.
By the way, we recommend an excellent article on customer needs, published on the HubSpot blog, "16 Types of Customer Needs (and How to Solve for Them)".
It helps understand how complex the structure of needs is. At the same time, it clearly shows that the funnel model can no longer be functional with such complex expectations.
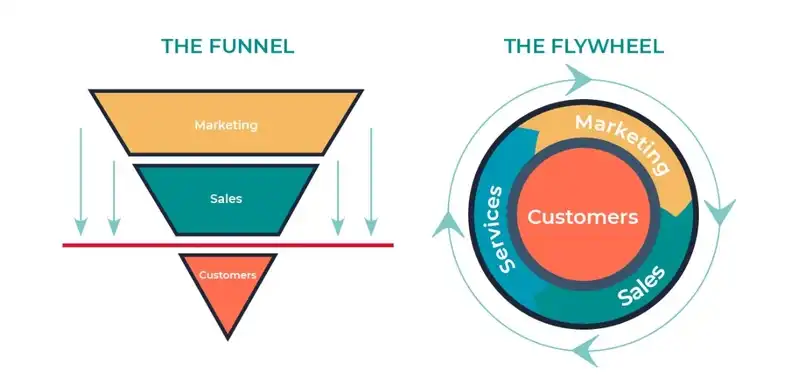
Flywheel vs. Sales Funnel — similarities and differences
The part that both models have in common is the focus on the "traveling customer" and their path and stages of this journey.
The sales funnel expresses hope and is an unconscious manifestation of sellers' and service providers' wishes.
It's an example of wishful thinking and patronization (if we guide you correctly, you will buy from us).
The linear path, whose goal is a purchase, should convert the potential customer into a real one. It should be clear as day that this model, in terms of time, is highly focused on short-term goals. It has a shallow time horizon and a minimal range of expectations.
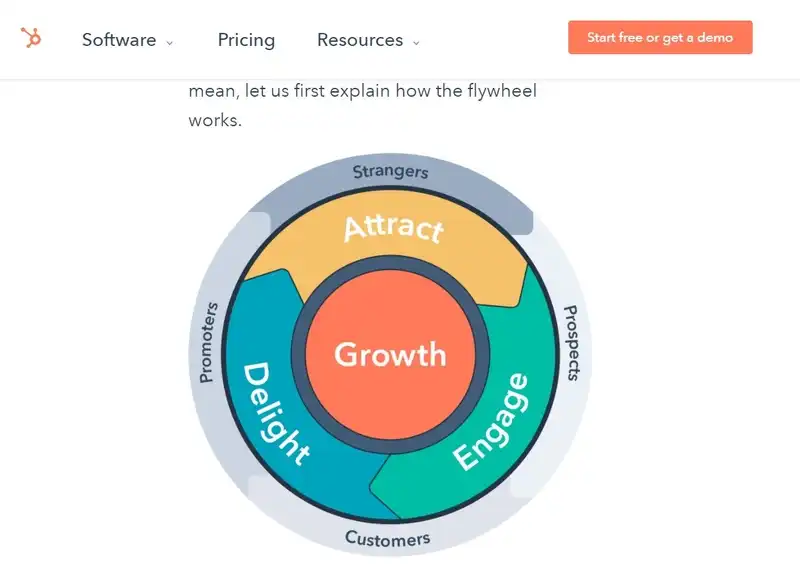
The flywheel metaphor replaces the linear path, finite in time and space, finite in goals, means, and consequences, with a circular movement with no beginning or end.
It's dynamic, open, always positive, and focused on a lasting, renewable, continuously built customer relationship and customer success.
The flywheel model is more about customer satisfaction than bar charts or the conversion rate percentage.
Flywheel focuses on building lasting relationships with customers, which are supposed to result in repeat purchases, spontaneous recommendations, and positive ratings. The customer, the user, is at the center of the company's marketing activities, just as the user is at the center of user-centered design.
The sales funnel is a model that is aimed at short-term goals. Flywheel is the opposite and concentrates on the organization's long-term objectives, effects, and business strategies.
The strength, the distinguisher of the flywheel model is that it focuses on three aspects:
- Attract
- Engage
- Delight
Attracting attention is oriented toward evoking emotions, gaining attention, and drawing the user or customer into the brand's world—the world of its values, uniqueness, and distinguishing features. You can attract customers by increasing inbound marketing efforts and using the power of social media marketing.
Engagement, in the case of digital products, means paying particular attention to the user experience. It's about ensuring a shopping experience that is seen and rated as friendly, pro-consumer, convenient, nice, pleasant, simple, and trouble-free. To achieve this effect, we need to listen to customer feedback.
To delight customers, you need to focus on reducing friction, reluctance, obstacles, problems, and barriers and offer proactive customer service. This increases the effectiveness of actions and is a method for improving and streamlining the performance, setting the wheel in motion.
UX flywheel or customer experience in the flywheel model
While the sales funnel model was focused on the course of a single process, which was then generalized through statistical repetition, flywheel seeks to repeat it.
However, not by looking for contact with a new, unique customer but with the one already acquired by the organization.
That's why creating content, operations, and functionality supporting renewed interaction is essential and conducive to building engagement and deepening and expanding relationships.
We'll use a well-known proverb to help you understand this concept: "A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush." The flywheel model is an ideal example of such an approach and way of thinking.
However, the acquired customer still requires special attention and expects appropriate engagement from the organization. They're the customer whose experiences, feelings, emotions, attitudes, expectations, and needs must be handled in a particular way.
Here, UI/UX design, UX research, customer research, and UX audit come to the rescue—an entire squad of tools, methods, techniques, approaches, patterns, standards, and solutions focused on the user and customer.
The body of knowledge, research, reports, design recommendations, and test results can be successfully used to implement a new path to purchase model, such as flywheel.
While the classic sales funnel model didn't consider the customer's satisfaction, positive emotions, impressions, and experience, the flywheel model focuses on diagnosing, researching, monitoring, and optimizing them.
For example, the user of a corporate website or an online store is the central figure in this approach. They need understanding, attention, and empathy.
Nowadays, users who are essential to the flywheel model are much more demanding. Their purchasing decisions are much more complex and multi-dimensional and come from different processes, situations, and conditions than a few decades ago.
Hence, acquiring and maintaining clients' loyalty is much more challenging and requires different approaches and tools.
Flywheel relies on having happy customers because they drive positive recommendations and repeat sales.
How to design and optimize UX in flywheel?
We have good news for everybody who thought during the reading of this article that using the flywheel model would mean a revolution and entail changing almost everything about how the organization works. There is no such need.

The implementation of the flywheel involves a change of mindset, a change of some activities, and a change of goals, priorities, metrics, and tools.
Does that sound scary? Fortunately, in practice, it is not. Flywheel is not a revolution but an evolution.
The most significant advantage of flywheel is that it doesn't involve the need to make revolutionary changes that most companies wouldn't handle regarding organization, awareness, or personnel.
So, what do you need to pay special attention to when adapting the classic sales funnel to the flywheel's logic?
When adapting the sales funnel, you should concentrate on the following:
- Creating and adapting personas — they should more accurately define and understand the customer and their loyalty and engagement.
- Friendliness, ease, understandability, obviousness, and speed of the path to purchase.
- Personalization and customization—the article "Customization vs. Personalization in the User Experience," published on the NN Group blog, is the most appropriate reading, and we recommend it.
- Proper error handling, understanding customers' preferences, types of clients, and their various needs (functional as well).
- Considering research and tests (customer research), defining critical problems from the perspective of customers and users of products.
- Changing the way of thinking and adopting marketing strategy and design assumptions based on the metaphor and the idea of the flywheel.
- Creating a business strategy focused on customer experiences (customer, user experience).
- Modifying content in terms of regular, loyal customers.
- Optimizing inefficient, unfriendly processes that affect customers' experiences and business growth.
- Applying user-centered design.
- Reducing cognitive frictions.
- Designing interactions (IxD) where the user needs play a critical role.
Flywheel — a new path to purchase model. Summary
- The sales funnel is a visual representation of the process, the potential customer journey in which the first contact with a brand, product, or company is the beginning, and the purchase of a product or using a service is the end.
- The sales funnel consists of 4 stages: awareness, engagement, desire, and action.
- It's a modified version of the AIDA model (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action).
- The sales funnel is often seen as archaic and inadequate for new situations and challenges modern organizations face.
- Critics of the sales funnel accuse it of being detrimentally focused on attracting the attention of as many potential customers as possible while neglecting those already existing.
- The sales funnel model is heavily focused on hard sales results. It overlooks essential issues such as building customer relationships and doesn't consider their needs, expectations, and emotions.
- It operates with simple indicators of success — purchase or lack of it.
- By absolutizing the sales result, the sales funnel ignores the potential of the relationship with the customer. It overlooks the opportunity that lies in stimulating customers to repeat purchases. They can become spontaneous, genuine brand ambassadors.
- In the era of customer, user, and experience supremacy, the sales funnel is increasingly replaced by a model that puts complex customer needs in the center.
- Flywheel is a new approach to the sales funnel model and the path to purchase.
- "A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush" — the flywheel is an ideal example of the thinking that this popular proverb summarizes.
- The flywheel idea is based on modifying, optimizing, and adapting the sales funnel concept to new market and technological conditions related to changes in customer expectations.
- The change proposed by the flywheel model is to move away from linear thinking about the path to purchase. Instead of thinking in — start/finish — categories, it proposes circular thinking.
- Circularity in flywheel means no beginning and no end.
- The flywheel metaphor replaces the linear path, finite in time and space, finite in goals, means, and consequences, with a circular movement with no beginning or end.
- In the flywheel model, more emphasis is put on fulfilling customer expectations.
- Traditional success metrics are being replaced by new ones or modified. While they lose their importance, they don't lose their relevance—they're still used as important but no longer the most important measures of success.
- Flywheel focuses on building lasting relationships with customers.
- The customer, the user, and the path to purchase are at the center of the company's marketing activities, just as the user is at the center of user-centered design.
- The main goal of the flywheel model (flywheel marketing) is to attract, engage, and delight the customer. The path to purchase (e.g., the e-commerce path to purchase) is still very important, but the emphasis is on its features that support the relationship's stability.
- The marketing team, sales team, and customer service team need to work together to create a positive customer experience.
- Flywheel is used to build relationships and engage clients. Acquiring and maintaining clients' loyalty is much more challenging and requires different approaches and tools.
- It's expressed by creating content, operations, and functionality supporting renewed interaction conducive to building engagement and deepening and expanding relationships.
- The implementation of the flywheel by the sales team involves a change of mindset, a change of some activities, and a change of goals, priorities, metrics, and tools.
- Flywheel is certainly not revolutionary. However, the effects of its implementation may cause such results.






