What is a Sales Funnel?
Sales funnel, marketing funnel as a design and optimization problem is of interest to many specialists.
Not only salespeople, marketers, and business owners are wondering how to build a Sales Funnel (Sales Funnel, Purchase Funnel, Marketing Funnel, Revenue Funnel).
The Sales Funnel is also a design, research, and optimization problem for UX/UI designers, UX researchers, and developers.
The goal of any digital business is to increase sales, scale, streamline the purchasing process, increase market share, and stabilize its market position.
The sales path and its modeling allow you to better understand the goals, problems, opportunities, expectations, and stages (along with their respective conditions and dilemmas) of the user and create better-tailored solutions.
As a side note, process modeling in marketing and user experience is a common and highly recommended activity.
Take the customer journey map, user journey map, defining personas, and service blueprint as examples.
While answering the question in this article — What is a Conversion Funnel, a Sales Funnel? — we will try to show the connections between sales volume and UX. We will also describe the problems, opportunities, and possibilities arising from these interdependencies.
When designing and optimizing the various stages of the customer journey, the stages in the Sales Funnel, you cannot lose sight of the experiences that accompany users and potential customers.
Different stages of the Funnel represent different sets of design problems needed to be solved.
How to optimize the different stages of the Sales Funnel? How to motivate, encourage, and engage users so that they want to move down the Funnel?
To what experiences, in particular, should you pay attention when designing and optimizing the Sales Funnel?
If you are curious, we invite you to take a journey down the Sales Funnel.
We wish you a pleasant reading!
A Sales Funnel — what is it?
Definitions are very important, so let's start by defining the sales funnel.
The sales funnel, purchase funnel — or whatever you want to call this model — is nothing more than a visual representation of the customer journey.
It is a path that a potential customer, who is interested in purchasing a product or service, travels.
In a visual sense, the funnel is an inverted pyramid, a metaphor that shows that each offer arouses more or less broad interest and causes, provokes to act (purchase) a certain number of users.
In other words, the effect, the final stage of the funnel is not only sales but any kind of conversion, any actions from the perspective of the interests and goals of a website owner that are desirable.
Hence, we can talk about the sales funnel and the conversion funnel — about supporting the purchasing process, presenting the products offered more effectively, and supporting the making of a purchase.
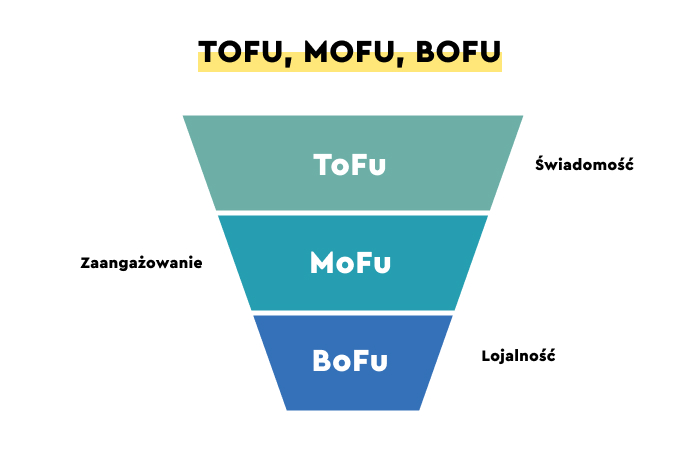
Sales funnels represent this journey in stages, which begins with an awareness stage and ends with an action stage.
The sales funnel is a concept that initially appeared in marketing, but it is also beneficial for creating digital products.
The funnel — although a somewhat misleading metaphor due to the reduction in the number of users who become customers rather than simply liquefying them — illustrates the path users must take to become buying customers.
Beware! The sales funnel is not about acquiring leads. It is a tool that supports the sales process, acquiring loyal customers, and is a way to achieve marketing success.
The length of the sales path is fixed in this model and consists of three parts: top, middle, and bottom. We will write about the various stages in a moment.
Now take a look at what the sales funnel can help you with:
- Helps you to understand the conditions of the user at a given stage
- Allows you to observe the typical actions for a given stage
- Enables you to develop solutions that are relevant to the condition, activities, and needs at a given stage
- Allows you to customize messages, functionalities, and channels
- It is formative and selective in nature
- Raises awareness of the task-oriented nature of the user's activities (e.g., the task may be shopping, but also exploring, learning about the offer, comparing offers, planning purchases that will be finalized in the future)
- Enables you to diagnose problems and invest in concrete solutions
- Allows you to optimize and thus expand its bottom part.
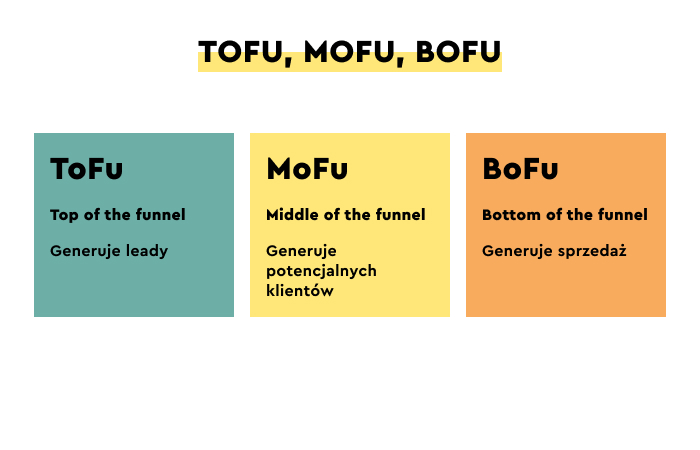
The sales funnel, in its most basic form, consists of three elements and includes:
- The top of the funnel: contains stages of awareness and discovery.
- The middle of the funnel: involves searching for solutions.
- The bottom of the funnel: boils down to making an informed buying decision.
In the case of digital products, the sales funnel model has been adapted to the specifics of online sales.
Of course, the clue of the tool remained the same. The division into three stages has also been maintained, with a greater emphasis on their specificity.
The sales funnel for digital products includes the following phases, stages:
- ToFu (Top of the Funnel): at the initial stage, the main goal is to arouse user awareness.
- MoFu (Middle of the Funnel): at this stage, it is crucial to know and define the specific location and condition of the user who is initially interested in the purchase or subscription.
- BoFu (Bottom of the Funnel): at this stage, all efforts should be focused on supporting the purchase decision, supporting conversion, and increasing sales.
At this point, it is essential to quote Dan Tyre, who, in the article "Sales Funnels: What They Are & What You Should Make Instead," notes that each funnel follows the same or very similar logic.
With that said. Every sales funnel:
- At the macro level, is characterized by a large number of potential buyers who are not yet thinking about finalizing the transaction.
- Has various selection criteria used by users of digital products that make the potential number of clients go down.
- Already in the middle of the funnel, the number of potential customers is reduced to a handful.
- The further the user is in the sales funnel, the more information they expect, and the clearer it becomes for them that using the product or service will be beneficial.
Of course, there are all sorts of modifications and variations of the basic funnel model, more or less elaborate. Still, the three-element model is the most influential, useful, and universal.
What are the stages of the Sales Funnel?
In an easy-to-understand visual format, the sales funnel helps people understand that a purchase is not a single action.
While it takes place at a specific time, on a specific day, and in a specific store, it is the result of a process that is stretched over time.
The finalization of the purchase is just the proverbial icing on the cake. A user rarely becomes a customer in an instant.
They go through three stages.
Top of the Funnel (ToFu) — Awareness and Discovery
Most users are at this stage. The awareness stage is aptly named after the state where users find themselves.
This is the first time they recognize a need and learn about the possibility of satisfying it with a particular digital product.
They can learn about a digital product or a digital service from a wide variety of sources: from advertisements, search engines, and mailings to word of mouth.
The user at this stage knows that digital products or services exist and that they could potentially be a good solution to their problem. Still, the user needs further encouragement to explore to see that this early intuition, and awareness, is correct.
The stage of arousing awareness and provoking, motivating, inspiring, and stimulating discovery, from the standpoint of user experience, is crucial.
This is related to the first impression effect.
In short, the first impression effect states that in as little as 50 milliseconds, the user will form an opinion and adopt a certain attitude toward a website, an offer, or, more generally, a digital product.
They will also feel encouraged or discouraged, become convinced that they have found the solution they were looking for, or the exact opposite.
They will think that even though the offer fits their needs, they will have to look for a better, more convincing, reliable, and trustworthy one.
You should remember that these reactions are automatic, not always conscious, repetitive, thoughtless, and grounded in assumptions, which consist of information, expectations, prejudices, stereotypes, ideas, norms and evaluations, and emotions.
That's why the first contact with a digital product should be a source of comfort.
The experience provided by the digital product should be consistent with the following:
- User needs (equally related to attractiveness and usability, aesthetics and functionality, emotions, and rational arguments)
- User expectations
- User experiences
- User's cognitive patterns
- Goals that the user wants to achieve
- Tasks that the user plans to perform.
Hence, the user should be, first and foremost:
- Comprehensively informed
- Effectively encouraged to enter the process through content, form, aesthetics, facts, pleasure and profit, benefits
- Guided, motivated, and rewarded (e.g., through gamification activities).
Middle of the Funnel (MoFu) — Researching Solutions, Evaluation
Users in this stage of the sales funnel become extremely active and independently seek information about ways to solve a given problem from those offered on the market.
This means that they need the following:
- Comprehensive but accessible information about the product or digital service. In the form of onboarding, tutorials, or case studies.
- Credible, reliable, convincing ratings and opinions (offered, for example, in Rating Systems).
- Substantive, objective, unbiased recommendations provided by independent specialists, expert institutions, and consumers (Third-Party Reviewers).
- Case Studies.
- Social Proof in the form of awards, certificates, and prizes.
- Trustmarks — which suggest meeting industry standards, affiliation with associations and guilds, and cooperation with trustworthy companies and institutions.
- Tools supporting filtering, sorting, comparing, evaluating, learning, and deciding.
All of these elements play a significant role at this stage as they sustain interest, support engagement, foster relationships, and arouse emotions.
They impact what users will think and feel, both in terms of the offer and the vendor, the digital product, and its creator.
At the MoFu stage, the interaction between the user and site representatives frequently occurs. Representatives should demonstrate particular openness, flexibility, empathy, commitment, and helpfulness.
Bottom of the Funnel (BoFu) — Purchase Decision
At this stage, it is crucial to support the purchasing process and make the purchase path as simple, fast, convenient, and safe as possible.
Refining this stage in terms of User Experience also means that the digital product card, shopping cart, navigation, purchase summary and confirmation, and payment forms must be given special attention.
You should be aware that at this stage of the sales funnel, it is very easy for people to abandon the purchase. It is a particularly sensitive and fragile stage from the point of view of the user's needs, expectations, and capabilities.
Although initially convinced, users may abandon the shopping cart and the payment process, postpone the purchase and use the wishlist function for different reasons.
The most common reasons for abandoning further purchases and finalizing the purchase include the following:
- Problematic nature of shipping costs, shipping method, or shipping service company.
- A small number of payment methods.
- Technical and technological problems — the site loads slowly, and payment is made on external systems and platforms, which creates distrust.
- Length, level of complexity, time-consuming, and high cost of interaction with the website and its interface.
- Low reliability of the payment and purchase finalization processes.
We wrote about the specifics of these problems in the articles: "How to Design a Shopping Cart?", "Product Page Navigation - Designing Navigation."
How to create a Sales Funnel?
How to create a Sales Funnel? It is a question that requires combining knowledge, data, research, testing, analysis, and design guidelines from several domains. From marketing and commercial domains to design related to UI/UX Design.
Creating a sales funnel means getting to know users profoundly in terms of the following:
- Needs and typical behaviors: this means creating their Personas that answer key questions: Who are the users we want to "convert" into customers? What is the main objective of users? What keeps users from getting what they want?
- Expectations: meaning the need to define and learn about experiences, reference points, goals, and objectives.
- Behavior: this involves tracking the behavior and the reactions of users at each stage, using metrics appropriate to that stage.
- Preferences: meaning getting to know users in terms of preferred communication language, quantity, type, data sources, tools, and functionalities.
- Emotional needs: involving the need to learn about what solutions regarding security issues users want.
- Aesthetic needs: the need to know aesthetic preferences, preferences in terms of graphic forms and styles (e.g., Flat Design).
Creating the sales funnel — you can't forget about it — is not a one-time activity but a work-in-progress operation. It is a process of ongoing investigation, diagnosis, analysis, optimization, and iteration.
In the article "Sales funnel: a definition," published on the Hotjar blog, you can find useful questions that help guide research, testing, and optimization.
When creating and optimizing the sales funnel, you should consider the following:
- What might be missing on the site from the users' perspective?
- What prevents users from buying?
- What are users looking for most often?
- How can the site be helpful to users?
You should consider the remark Michael Bosworth made in his book "Solution Selling: Creating Buyers in Difficult Selling Markets."
Bosworth is more than certain that effective sales, effective sales funnel design is about something entirely different today than it used to be.
Once upon a time, effective selling was all about persuading, convincing, overcoming resistance, dealing with objections, and closing the sale.
Nowadays, sales are more focused on helping. The customer must be supported in achieving a goal, solving a problem, or satisfying a need at every stage.
How to design a Sales Funnel? Summary
- The sales funnel, the marketing funnel, poses a marketing problem, a sales problem, a design problem (UI/UX Design), a research problem (UX Research), an optimization problem, and a technology problem.
- The sales path and its modeling allow you to understand better the goals, problems, opportunities, and expectations of the potential customer during the sales process.
- Designing the sales funnel (e.g., e-Commerce sales funnel, b2b sales funnel) allows you to implement solutions on your website that better solve your users' problems and needs.
- It also helps to rationalize the selection of sales techniques, create more effective sales pages, improve marketing activities, and understand how potential customers feel at different stages of the funnel.
- The sales funnel is a metaphor. It makes you realize that awareness of the product is insufficient for successful sales.
- Building interest as early as the first stage of the funnel (e.g., in the E-Commerce industry) and at subsequent stages of the funnel, getting the audience interested if only on social media and gaining attention (e.g., through an advertising campaign) increases sales opportunities.
- The ideal sales funnel illustrates the path (at every stage of the sales process) that customers interested in the offer have to go through to become buying customers.
- The sales funnel (e.g., the sales funnel in an online store) in the case of digital products includes three stages: ToFu (Top of the Funnel), MoFu (Middle of the Funnel), and BoFu (Bottom of the Funnel).
- ToFu stage — the user at this stage knows that digital products or services exist and that they could potentially be a good solution to their problem. Still, the user needs further encouragement to explore to see that this early intuition, and awareness, is correct.
- MoFu stage — the user, at this stage of the sales funnel, actively and independently seeks information on ways to solve a given problem from those offered on the market. They want to know as much as possible about the offer and are looking for additional information necessary to make a purchasing decision. Time-saving is also quite important here.
- BoFu stage — the user should be particularly supported at this stage. Finalization of the purchase should be as simple, fast, convenient, and secure as possible.
- Once upon a time, effective selling was all about persuading, convincing, overcoming resistance, dealing with objections, and closing the sale.
- Nowadays, sales focus more on helping the customer achieve a goal, solve a problem, or satisfy a need.