Diabetes comes in five types Type 1, Type 2, Gestational (pregnancy), LADA, and MODY, and is one of the leading causes of death worldwide.
It's a disease that chronically affects more than 400 million people (about 31 million in the USA).
Diabetes. A chronic disease of civilization. A condition that must be kept under control every day.
A disease that affects people all over the world, regardless of the affluence of society. According to the WHO website, the occurrence of Type 2 diabetes has increased dramatically over the past three decades in countries of all income levels.
It's a disease we've already written about in the article "Color vision disorders of interface (UI) users. Accessibility of interfaces for people affected by common diseases". We discussed in it the relationship linking civilization diseases, including diabetes, with User Experience and UI Design.
Mobile applications in medicine also include apps that allow people with diabetes to manage better the daily challenges associated with the disease.
They're in constant supply thanks to their usefulness, safety, and utility. Demand for them is also increasing.
In the Google Play Store alone, we'll find 247 apps displayed when we type the keyword "diabetes." Over time, their number will increase rather than decrease.
Mobile apps for people with diabetes (and animals – they can get sick, too) are very popular not only because of the number of patients but also because of the usefulness of this kind of software.
How should mobile apps for people with diabetes meet the needs and expectations of patients? What kind of User Experience should app designers offer? Finally, what functionalities should be included in a mobile app to help people with diabetes?
We'll answer those questions in a moment. We invite you to read the article.
What kind of disease is diabetes?
As we mentioned, diabetes is primarily a chronic disease. It's a metabolic disease characterized by elevated glucose levels in the blood.
A disruption in insulin secretion by the pancreas causes it. Too little or too much insulin produced by this organ is very harmful. In fact, it's extremely dangerous for the organism.
As a consequence of pancreatic dysfunction, other organs are damaged, most notably the heart, eyes, and kidneys.

Untreated diabetes is a disease that directly endangers a person's life. Treated diabetes means regularly tracking glucose, taking insulin, and maintaining a particular diet, exercise, and mental health hygiene regime.
Physical activity and adequately selected, prepared, and portioned meals are crucial to the course of the disease and the well-being of a patient.
They also affect the course of numerous diseases that coexist with diabetes. Primarily on the course of depression, heart disease, and chronic fatigue syndrome.
It can be difficult for patients to monitor and document their sugar level results independently and consistently and to see the cause-and-effect relationships between exercise, diet, sugar, and insulin levels.
It's undoubtedly much easier if supported by the right tools, such as mobile apps for people with diabetes.
Mobile apps for patients, such as mHealth, change how chronic diseases are treated
Mobile health (mHealth) has brought a new quality to how diabetes patients are treated. mHealth includes not only apps dedicated to a particular disease (in this case, diabetes) but also offers increasingly extensive and comprehensive health care and treatment systems.
Devices, technologies, and users are being combined and integrated to not only improve daily care but also to study the quality, patterns, and problems of everyday care and optimize and discover new ways to solve health problems.
Mobile applications for people with diabetes, although already based on standard, conventional modules, will be further developed in the search for innovative technologies and solutions.
With the development of mHealth, healthcare and patients' quality of life has changed, as they can more independently and individually monitor the course of their disease.
Thanks to mobile applications, it's possible to communicate, exchange, and synthesize information more conveniently and efficiently. Thanks to the information collected daily, the picture of the disease, its dynamics, and its peculiarities is much more precise and valuable from a medical point of view.
The data considered collectively also make it possible to make medical discoveries – find previously unseen regularities, symptoms, and relationships.
Design and development of a mobile application that supports the treatment of diabetes
Our goal should be to develop a commercial or free application for patients' self-monitoring that allows them to remember sugar levels and determine optimal insulin doses.
The axis of a mobile application for people with diabetes is to capture and adequately visualize the relationship between:
- Food (glycemic index)
- Physical activity
- Blood sugar levels
- The number of insulin doses taken.
A mobile application for patients with diabetes – in its most typical and basic form – allows them to:
- Record glucose levels in the blood, measure body weight and insulin units
- Download data from other apps (e.g., wellness apps that are used to monitor and analyze physical activity)
- Track progress, stages, treatment, and therapeutic goals
- Synchronize the app with external devices (e.g., glucometer)
- Remind the patients to take their medication regularly
- Quickly contact medical personnel
- Create a disease picture (by entering data on past and treated diseases or allergies)
- Learn by offering information about the disease, its course, treatment methods, and medical news
- Improve the daily life of a person with diabetes.
Expanding the knowledge and awareness about diabetes through a mobile application dedicated to people afflicted by this disease allows users to gain an additional benefit.
Awareness of the disease's course, dependencies, risks, and ways to deal with typical problems makes the treatment process more focused, rational, and effective.
What's more, regularly offered tips, trivia, and advice (Diabetes Life Hacks) allow us to better cope with the disease, and they also have a therapeutic function because they are a type of support.
It's also essential to offer communication between a patient and an attending physician.
Directness, access to all data (especially sugar levels), measurements, results, and the ability to track their changes over time, along with other vital factors, variables, and indicators, is a very helpful tool for doctors. All of that supports making diagnoses, adopting treatment strategies, and making decisions about changes in prescribed drugs and dosages.
Graphic design of mobile apps for people with diabetes also requires reinforcement through functionality, design, aesthetics, and gamification of user engagement.
A mobile app for patients with diabetes should respond to their needs, and these include the following:
- Ability to record the results of blood glucose tests (it's usually necessary to perform them several times a day and record the results – usually in the form of a dairy)
- Record weight measurement results
- Save the results of blood pressure level
- Possibility of tracking and encouraging physical activity
- Ability to regularly take medications
- Regularly eat well-balanced food that keeps glucose levels stable.
Offering and using the above functionalities improves the quality of a patient's daily life. It makes it possible to make changes in treatment that can reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
For example, they can reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
Modern mobile applications – additional functionalities of apps for people with diabetes
Mobile apps, including those offered to people with diabetes, are increasingly going beyond the typical set of functionalities and provide capabilities to streamline needs of varying priority of importance.
The set is constantly expanding, turning diabetes applications into tools that provide a multidimensional, multifaceted, and holistic approach to the problem of prevention and treatment of diabetes.
They make it possible to manage better the pro-health steps taken, plan treatment activities, and evaluate their results.
In mobile apps for people with diabetes, users are offered the opportunity to:
- Print data and documents
- Share data on different platforms, operating systems, different devices, and with different users (e.g., family members, caregivers)
- Create a community
- Communicate via instant messaging, post on dedicated forums
- Set health goals, for example, related to physical activity
- Participate in research processes, test groups
- Personalize the app – customize it according to the type of diabetes, the specific needs of a given user
- Get advice from specialists – not only diabetologists but also nutritionists, fitness trainers, and psychologists (depression and anxiety disorders frequently co-occur with diabetes)
- Make calculations in BMI calculators and glycemic load calculators
- Scan barcodes providing information about the content of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, and sugars in a given food
- Generate reports, spot trends, and regularity in symptoms
- Create medication lists, schedules, and instructions
- Create alerts to help patients take their medication on a regular, consistent basis
- Use prescription assistants
- Receive discounts on pharmacy purchases awarded to the most engaged users.
A responsive mobile app in medicine not only needs to offer a set of functions, a real benefit (accurately control basic results, facilitate measurements, product selection), and be secure, but should also be engaging.
Very often, this goal is achieved with the help of gamification, the best examples of which are all kinds of activities that provide discounts.
Mobile apps for people with diabetes raise issues
However, we must add a spoonful of tar to this barrel of honey, but a small one. While the benefits of using mobile apps in medicine are pretty compelling, they still have drawbacks.
The design and, above all, development of mobile applications for patients with diabetes raises peculiar problems.
For example, they relate to technological relevance and debt, compliance with operating system requirements, and the need to update applications. Their reliability, stability, and compatibility are also important.
Making them as error-free as possible is essential, especially regarding processing personal and medical data.
Equally important are data security issues. As we read in the article "Diabetes Digital App Technology: Benefits, Challenges, and Recommendations," diabetes apps have been sharing data with third parties on a massive scale.
That's why developers or business owners should implement and diligently enforce special privacy policies to guarantee patients and users a sufficiently high-security standard.
Special solutions for data security and data confidentiality should mean, among other things, that users can fully control them.
We should only share data with third parties with users' full awareness and consent.
Privacy and increased data protection should become a design, business, and market standard.
All the more so because the leakage of such data or the release of such data to unauthorized third parties can consequently cause a lot of individual and society-wide damage.
For example, they can result in discrimination in the labor market.
Trends in mobile applications – mobile apps for dog and cat owners
When writing about mobile medical apps and mobile apps for people with diabetes, it's impossible not to mention the emerging trend of developing apps for animals.
The demand for mobile apps increasingly translates into demand for apps supporting the care of animals with chronic diseases.
Like apps developed for humans, apps dedicated to animals have the same typical functionalities.
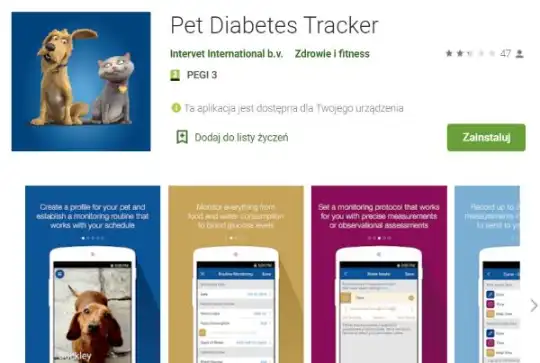
Mobile apps – mainly aimed at dog and cat owners – allow pet owners to enter data on their pet's blood glucose levels, amount and type of food consumed, water drunk, body weight, and pet physical activity. Apps also allow users to send reports to veterinarians.
Diabetes doesn't just affect humans, but year after year, decade after decade, it's becoming an increasingly severe problem for pets, mainly dogs and cats.
Obesity of pets, one of the most important causes of diabetes in animals, affects almost half of the domestic animals.

The phenomenon of pet familiarity, the prevalence and the availability of veterinary services, and the number of pets cause an increase in the segment of apps supporting the treatment of diabetes in animals.
Applications for people with diabetes. Summary
- Diabetes is a metabolic disease, chronic in nature, which is caused by a malfunction of the pancreas, resulting in elevated levels of glucose in the blood. It involves measuring sugar levels (blood glucose levels) in everyday life.
- More than 400 million people worldwide have diabetes.
- In the USA, about 31 million people.
- Mobile medical apps, including mobile apps for patients with diabetes, are becoming increasingly popular due to their usefulness, safety, and usability; also, their number on different platforms is constantly increasing.
- Mobile health apps (mHealth) have brought a new quality to how diabetes patients are treated. mHealth offers increasingly extensive and comprehensive health care and treatment systems.
- Mobile apps for people with diabetes have become popular due to their usability and the ever-growing number of patients. Diabetes is a disease of civilization.
- It can be difficult for a patient to independently and consistently monitor and document the results of measurements and tests.
- Mobile apps for people with diabetes make these necessary daily activities much simpler and more convenient.
- The main benefit of using a mobile app for people with diabetes is to capture and adequately visualize the relationship between food, physical activity, blood sugar levels, and insulin doses.
- Mobile apps for people with diabetes primarily allow them to record blood glucose results, download data from other apps, track progress, stages, treatment goals, and therapeutic goals, and synchronize the app with external devices (such as a glucometer).
- Awareness of the disease's course, dependencies, risks, and ways to deal with typical problems makes the treatment process more focused, rational, and effective.
- Access to data, measurements, results, and the ability to track their changes over time is a very helpful tool for doctors to support diagnosis and treatment.
- In the graphic design of mobile apps for people with diabetes, it's also important to reinforce user engagement through functionalities, design, aesthetics, and gamification.
- Mobile apps, including those offered to people with diabetes, are increasingly going beyond the typical set of functionalities and provide capabilities to streamline needs of varying priority of importance.
- The interface design of mobile applications, especially mobile applications for people with diabetes, raises peculiar problems. For example, they're related to technological relevance, compliance with operating system requirements, and the need to update applications.
- Critical issues in terms of trust in applications also include their reliability, stability, and compatibility. Last but not least, recommendations by external institutions that can confirm their safety for the patient are also essential.
- To ensure a sufficiently high standard of security for patients, we should implement and diligently enforce special privacy policies.
- Special solutions for data security and data confidentiality should mean, among other things, that users can fully control them.
- We should only share data with third parties with users' full awareness and consent.
- Privacy and increased data protection should become a design, business, and market standard.
- Mobile apps for animals with diabetes have the same typical functionalities as those dedicated to humans. Diabetes apps increasingly include apps used by dog and cat owners.
- Mobile apps for pets with diabetes allow their owners to enter key data. Apps also allow users to send reports to veterinarians.
- The phenomenon of pet familiarity, the prevalence and the availability of veterinary services, and the number of pets cause an increase in the segment of apps supporting the treatment of diabetes in animals.



