Mouse Tracking/Cursor Tracking and Mouse Heat Maps are research methods used in the usability testing of web applications.
Cursor Tracking allows us to discover behavior, reaction, and interaction patterns in how web app users interact with its interface.
Thanks to it, we can better understand what problems users are facing.
It's not just about problems involving functionality but also content, page layout, navigation, and interface.
A mouse heat map is a type of thermal map (used, for example, in eye tracking research) that graphically visualizes the intensity of actions performed (like scrolling or pausing).
UX researchers are increasingly interested in this method and are incorporating it into their standard usability research corpus, thanks to the dynamic development of research tools.
Mouse heat maps and cursor tracking helps discover attention patterns and usability problems. They're methods that form the basis for optimization activities aimed at improving the Conversion Rate.
How exactly do the mouse heat map and cursor tracking work? What are the advantages of these methods? What is the difference between mouse tracking and eye tracking?
How can mouse heat maps and cursor tracking be useful to UX/UI Designers? What are the limitations of these methods?
If you're curious about the answers to the above questions, we cordially invite you to read our article.
What is Mouse Tracking?
Mouse tracking is a UX research method that uses special software that allows us to track, aggregate, and compare data representing user behavior on a site (e.g., exploring a specific area).
The basic premise of this method is to draw attention to the relationship between website usability and mouse usage patterns.
![]()
How we use a mouse indicates how helpful or problematic a website is in terms of usability.
Examining elements using this method allows us to make changes (for example, to the main menu) and create a website with high usability.
Mouse tracking makes it possible to create a visual representation of the behavioral patterns of website users and to identify the elements of the website that attract the most attention and those that are indifferent or less popular (such as additional buttons).
This method is also used to discover conversion blockers and interface elements with which interaction is problematic in the following dimensions:
- Cognitive
- Manual (such as drop-down menus)
- Function
- Logical (such as making a purchase)
- Compliance with current design patterns.
Mouse tracking is often a beneficial supplement to eye tracking studies. We should remember that eye tracking research has its limitations.
First of all, it requires specialized equipment, is expensive, and raises questions about the naturalness of the site's browsing environment.
Studies involving mouse tracking are much less expensive, don't require specialized equipment, and are conducted under much more natural conditions (from the point of view of the website user being studied).
Cursor tracking can help diagnose where the user's attention is focused, especially since the cursor is often used as a tool to assist in reading and scanning the content of a page.
Mouse tracking is an essential supplement to studies that measure the number of clicks. Clicks are the primary or definitive point of attention for visitors but not the only one.
User behavior on a website also includes indirect actions that can affect individual clicks or cause refraining from performing an action.
In the article "What can a mouse cursor tell us more? Correlation of eye/mouse movements on web browsing," the study results were presented according to which, when both methods of testing are conducted simultaneously, there is an 84%-88% correlation in outcomes.
According to the article's authors, there is a strong relationship between the position of the gaze and the cursor position.
In addition, there are regular patterns of eye and mouse movements.
Mouse heat maps can provide additional, very useful information about how users interact with websites.
Mouse movements allow us to see points of interest that don't result in clicks and help reconstruct a website user's perceptual and decision-making process.
They make it possible to understand users' intentions and goals and how they achieve them (e.g., improving visibility).
In web analytics, heat maps also have a high diagnostic value in terms of clarity, fluidity of actions, orientation, and user confusion in the structure and layout of a given page.
Combined with another research technique, the Think Aloud method, it's possible to gain a better, more accurate understanding of user reactions and the problems that potential customers encounter.
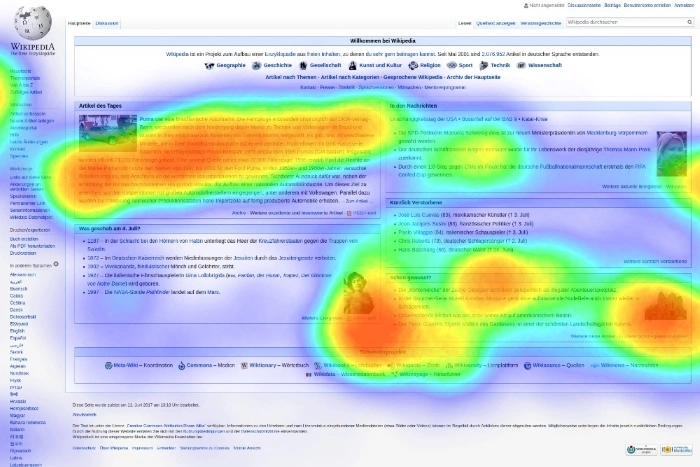
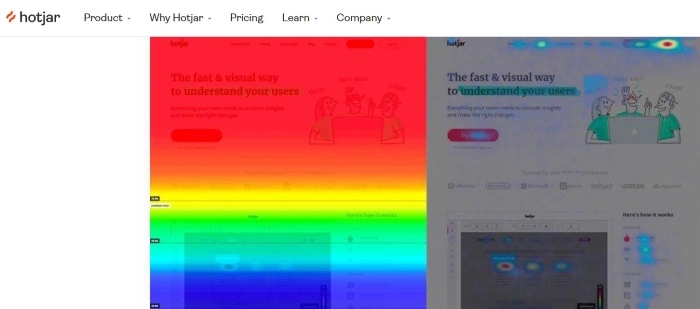
Mouse Heat Map. Heatmaps in UX
Mouse heat maps are visual representations of a website user's interactions with its interface.
They're used to increase the conversion of individual elements (e.g., justify their relocation).
Often, mouse heat maps also function under the names: mouse tracking heat map, mouse movement heat map, mouse hover map, attention map, attention heat map, or movement map.
According to the standard color convention, the intensity of the red color indicates a large number of user actions, and the blue color indicates the absence of any action. The other colors represent the spectrum of this scale.
Mouse heat maps also show areas on a website, sections of a site that are of no interest and that users don't interact with, which is helpful in user experience design.
By analyzing the colors on a heat map, we can discover the following:
- Frustration points on a site
- Points of distraction
- Reading patterns
- Behavioral patterns (e.g., click or scroll sequences)
- The intensity of engagement in interaction
- The extent of exploration of a website (in particular, this is important for extensive pages that require long scrolling)
- Real behaviors that provide data that can support design and optimization decisions
- Problems in interacting with functionalities on a website (e.g., forms)
- Processes (e.g., defining mouse flows).
Simultaneously mouse heat maps allow us to:
- Diagnose the usability of websites
- Determine the most optimal position for given functionalities, content, and user interface elements
- Evaluate the navigation performance – they help us see if users navigate the website smoothly, or if they search for links or have difficulty navigating the site
- Improve comfort and user experience in terms of security, credibility, and trust
- Create alerts and prompts in the most optimal places
- Diagnose reading patterns (F-Shaped Pattern of Reading) and determine the layout pattern (Z-Pattern Layout).
What is the difference between Mouse Tracking and Eye Tracking? Types of Heat Maps
In principle, both types of research involve tracking. Mouse tracking involves following and graphically representing the mouse and cursor movements.
Eye tracking involves monitoring and graphically mapping the movement of the eyeballs.
Both methods aim to diagnose the elements that attract users' attention, arouse their interest, and provoke interaction.
They represent information in a positive sense (occurrence of interaction) and a negative sense (absence of interaction).
In a technical, methodological, and cognitive sense, the two methods are significantly different from each other and should be treated as complementary rather than competing methods.
The most important differences between mouse tracking and eye tracking come down to the following issues:
- Budget (eye tracking is a much more expensive method)
- Technical (mouse tracking is much simpler in terms of technology and doesn't require specialized equipment)
- Organizational (eye tracking is a method much more challenging in terms of recruitment and conducting a survey)
- Credibility (mouse tracking is much more natural and similar to real user behavior, in addition, due to its lower cost, we can increase the sample size)
- The influence, the so-called observer effect, the Hawthorne effect (eye tracking is a method in which this effect is much stronger).
While both methods are not without limitations and flaws, we shouldn't favor one over the other.
We should study a website from multiple angles and through diverse methods (e.g., a scroll map). Only then can individual elements be optimized (for example, to achieve navigation improvements).
Eye tracking, through the use of specialized equipment, makes it possible to capture involuntary behavior resulting from specific automatic reactions and actions taking place outside of the user's full awareness but affecting the course of their interaction with a website.
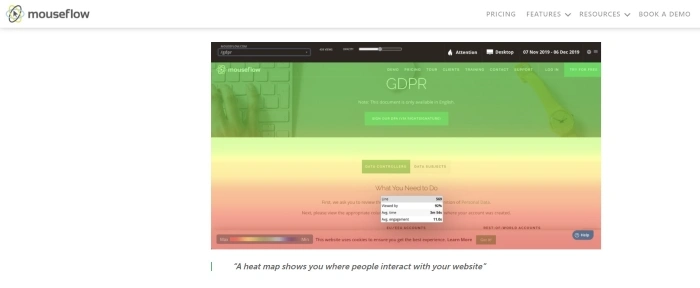
We should also remember that eye tracking includes following the peripheral vision, which isn't insignificant.
Mouse tracking, on the other hand, allows us to get better insight into users' intentions on our website and discover and understand voluntary actions.
These two methods also differ significantly in terms of competence, experience, and knowledge necessary to interpret the research results correctly.
Eye tracking is a much more specialized method and requires this kind of knowledge. We simply need to know what we're doing when it comes to tracking eye movements.
Mouse tracking doesn't cause such problems and is much more cognitively accessible to those without specialized equipment and experience in conducting, analyzing, and interpreting User Experience research results.
Why should we use Mouse Tracking and Mouse Heat Maps?
Perhaps the most obvious benefit of using this research method is the ability to make a website much more:
- Useful
- Friendly
- Intuitive
- Easy to use
- Understandable.
In addition, heat map analysis gives insight into the natural behavior within the site structure.
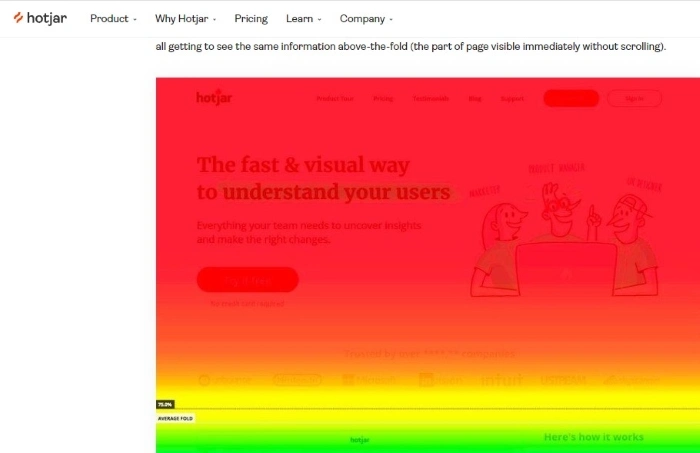
The high credibility of the research and its results makes it possible to assess to what extent the website raises problems in terms of:
- Function
- Information
- Navigation.
Some of the most important elements that we can optimize with mouse tracking results include the following:
- Interactive functionalities
- Links
- Menus (especially the drop-down menus)
- Scrollbars
- Text blocks
- Forms (e.g., credit card forms)
- Pagination
- Page template.
Mouse tracking also allows us to discover the following:
- Attractors and distractors – elements that attract attention and cause distraction
- Error-generating elements
- Previously unknown use cases
- Elements that support User Flow on websites
- Elements that favor or hinder reading and scanning the content of a page
- Elements that improve as well as decrease conversion rate results within the site.
UX Research based on tracking also helps:
- Speed up design and business decision-making processes
- Justify decision-making with data
- Make decisions based on representations of real behavior rather than perceptions of it
- Discover the navigation process
- Make interface changes that reduce interaction costs
- Discover patterns of repetitive behavior, choices, and usage scenarios
- Deduce the reasons for the effectiveness, or failure, of crucial conversion elements (e.g., Call To Action)
- Discover and resolve the issue of Rot and Broken Links.
Mouse Tracking. Mouse Heat Maps. Summary of the article
- Mouse cursor tracking, mouse heat map is an increasingly popular research method, especially in usability testing of web applications (UX Testing).
- Its purpose is to record the actual behavior of website users.
- Mouse tracking, a heat map analysis, is a method that helps to understand in a much better way (than, for example, a click map) what problems users face.
- Cursor tracking helps discover attention patterns and usability problems.
- This method often forms the basis for optimization activities that significantly increase conversion (Conversion Rate).
- Cursor tracking is a research method for aggregating and comparing information about user behavior.
- The basic premise of this research method is the idea that the way we use the mouse is an indication of how useful, or problematic in terms of usability, a website is.
- Mouse tracking allows us to create a visual representation of the behavioral patterns of website users.
- Mouse movements help reconstruct the perceptual and decision-making process of a website user.
- Mouse heat maps are visual representations of a website user's interactions with its interface.
- They also show the parts of a website that are of no interest.
- Mouse tracking and eye tracking studies are complementary, not competitive, methods.
- Both methods aim to discover the elements that attract users' attention, arouse their interest, and provoke interaction.
- Eye tracking allows us to capture involuntary behavior resulting from automatic actions taking place outside the user's full awareness.
- It's useful to use heat maps to understand better the intent with which users arrive on a site and their actions.
- Tracking-based research (e.g., tracking page scrolling, tracking cursor movements) helps justify the decision-making process (regarding business and design).
- In web analytics, heat maps are used very often.
- In addition, mouse heat maps help to make decisions based on representations of natural behavior and discover the navigation process.