Our Process
Functional Requirements

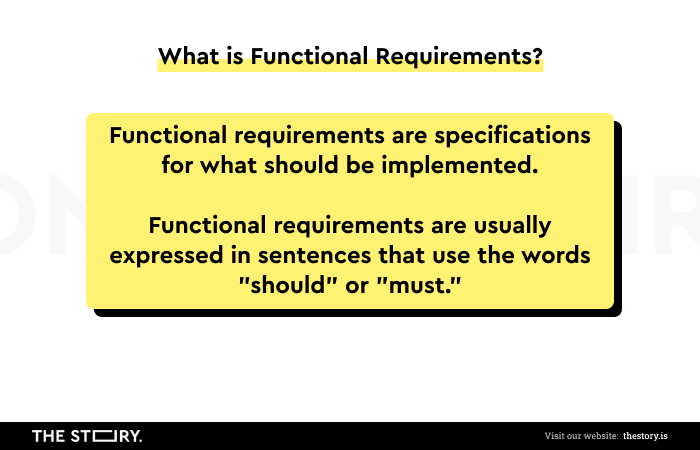
What are the functional requirements? Functional requirements are specifications for what should be implemented.
Functional requirements are usually expressed in sentences that use the words "should" or "must."
Some functional requirements examples can look like this:
"The mobile application should offer the ability to create a user account."
"The online store should offer the option to track the order delivery process."
"The website must allow users to sign up for a newsletter."
Functional requirements describe how software (e.g., mobile or web application) should behave. They also define the properties or attributes of a given system.
A typical functional requirement consists of a unique identifier, a summary, and a rationale. It is usually incorporated into user stories and use cases.
You should also remember another function, the role of functional requirements, which imposes constraints on the system development process.
In other words, functional requirements define the actions the application will perform in certain situations.
What are the functionalities of a digital product?
Functionality is one or more software capabilities that are meaningful to the user. For example, the bank's mobile app functionality is the ability to transfer or check an account balance.
It's also worth remembering that a single functionality, from the user's point of view, can be a set of functional requirements. This requirement can translate into several functionalities in the system that allow a given task to be performed.
At the same time, each stakeholder's list of functionalities doesn't necessarily coincide, which is why the business analyst should confront and coordinate the various expectations.
The business analyst's role is to comprehensively compile the various requirements into a software requirements specification (SRS).
In turn, the role of the SRS is to unambiguously and comprehensively describe a system's behavior. The specification is also very useful when testing and evaluating the quality of digital products created.
What problems does the lack of functional requirements create?
According to many authors (and such estimates dominate the literature on the subject), up to 50% of all mistakes that occur during software development are caused by a lack of requirements. Functional requirements allow this value to be significantly reduced.
Their quality is also problematic. The significant inaccuracies, lack of specificity, and unreliability present in them have an equally severe and negative impact on the quality of future software. How the requirements of a future web or mobile application are communicated dictates how the requirements are understood, defined, and ultimately implemented.
Incomplete, unclear information provided to each other by stakeholders and gaps in the specification and management of functional requirements significantly impact the workflow and its outcome.
The application's functional requirements mainly depend on communication, mutual understanding, agreement, and balancing various stakeholders' different goals, interests, and expectations.
Stakeholders are simultaneously the company's customers, application users, application owners, business analysts, developers, and designers.
And this means that we are dealing with a mixture of diverse, often contradictory:
- Needs and expectations
- Languages, ways of definition, and understanding
- Priorities
- Objectives and ways to achieve them
- Competencies
- Communication styles.
With such a diverse mix, it's very easy to have misunderstandings, disagreements, and frictions.
Hence, overlapping or conflicting interests must be adequately communicated, analyzed, considered, prioritized, or, generally speaking, managed.
The functional requirements of a web application are helpful from a development point of view and also help manage the project. Hence, developing and consistently applying methods that allow you to create products efficiently and error-free is necessary.
A very significant issue is the time dimension of functional requirements.
It's worth remembering and specifying whether the functionality will be implemented in the present or the future (preferably at a precisely defined point).
The time gap separating the present from the future (the planned application development) also introduces the need to rank and prioritize a given functionality.
Functionalities that will be implemented soon should receive high priority, and solutions whose implementation has not yet been clearly decided on should receive low priority.
What are the types of requirements for application development?
Requirements that are collected in the process of software development can be divided into three types:
- Business requirements
- Functional requirements
- User requirements
Each of the above types is accompanied by several non-functional requirements, which most often relate to the quality of future software (also known as quality attributes) and describe, among other things, performance requirements such as speed or security.
Business requirements
As the name suggests, business functional requirements refer to requirements formulated by business owners who create a digital product to achieve specific goals and business results.
Characteristics of business requirements include the following:
- Concentrating on business goals
- Providing a full view of a project
- Leading a project direction
- Matching business direction with the software
- Making sure software implementation matches customers' expectations
- Determining the results and benefits of the solution
User requirements
User requirements specify the tasks and goals the application's users can perform and achieve. They also indicate the application's expected and desired attributes. They encompass different types of requirements. In short, they're a broader term that describes functional, non-functional, and business requirements.
Functional requirements
Functional requirements define basic features and describe a system's desired behavior in particular situations.
Functional requirements allow you to:
- Define the product features
- Determine system behavior
- Describe administrative functions
- Set authentication levels
Proper coordination, orchestration, and harmonization of all three types of requirements are essential. This increases the probability of delivering a project on time without problems and minimizes the risk of failure.
How are the functional requirements of a web or a mobile application created?
A functional requirements document doesn't necessarily have to take the form of a printed piece of paper.
Nor does it necessarily have to take digital format in the form of files and folders.
It's helpful to think of functional requirements as a kind of container. The metaphor of a container captures the nature of functional requirements, which can take very different forms—both material and intangible.
They can be a sentence, a chart, a data set in a spreadsheet, a database, or any other information available through various media.
Identifying, collecting, analyzing, evaluating, documenting, and confirming requirements is crucial in the process of creating them.

Analysis, validation, and iteration of functional requirements
The purpose of the functional requirements analysis is primarily to understand and define the requirements placed on the software by the various stakeholders.
It's worth remembering that functional requirements aren't autonomous and are interdependent with quality expectations, goals, and business rules.
In addition, after analyzing functional requirements, we should rank individual functionalities, determine their importance, and link them to specific software elements.
Requirements validation aims to verify that the collected requirements are complete and error-free.
It should also provide an answer to whether the collected information allows you to start working and create a digital product that can achieve your business goals and align with users' expectations.
To obtain the fullest, most useful functional requirements, iterate them, that is, undertake a regular, cyclically repeated process of collecting, analyzing, and validating them.
An iterative approach to functional requirements allows you to understand them more thoroughly and accurately. It also helps to clarify, concretize, and confirm the requirements successively.
How to manage functional requirements?
Functional requirements can also be viewed as a process.
From this perspective, it is possible to manage them, and this is particularly true for:
- Defining a functional requirements database
- Assessing the impact of changes
- Maintaining consistency between the stages of the project and individual requirements
- Defining the dependencies and conditions occurring between individual requirements (also between a functional and non-functional requirement)
- Establishing tasks.
Generally speaking, the goal of requirements management (especially functional requirements) is to predict the impact that will result from the introduction of given changes.
Of course, it is also about improving communication and the flow of work and tasks.
Advantages of creating functional requirements
Although creating functional requirements is time-consuming and work-intensive, it's also worth doing—not only to minimize the risk of errors but also to improve the quality of work.
Creating functional requirements allows you to:
- Reduce the cost of creating a digital product
- Obtain a Single Source of Truth
- Reduce the number of stakeholder meetings
- Rationalize the work and allow you to give it a time frame, also in terms of roles, competencies, and responsibilities
- Reduce the number of revisions
- Manage time and deadlines better
- Decrease the number of unnecessary or unused functionalities
- Reduce the cost of digital product development
- Reduce the number of errors that occur during communication
- Control the chaos and organize the course of the project
- Improve work atmosphere and increase stakeholder satisfaction
- Last but not least, it allows you to create digital products according to expectations.