There is no need to explain to anyone what a mobile application is. Each of us uses at least a dozen such programs daily.
On a global scale, the statistical mobile phone user has about 80 applications installed.
Things are entirely different when we ask ourselves: How much does a mobile app cost? Nothing here is, and probably never will be, so obvious and unambiguous.
For a simple mobile app, the mobile app development cost ranges between $10,000 and $60,000. As the complexity increases, the app development costs reach $150,000 and even $300,000.
Of course, the price range also depends on the choice of app development companies since their pricing will vary.
Every mobile application is different. We'll encounter many false beliefs and myths about its creation, development, and maintenance. The cost of such work stirs up many emotions and leads to temperamental judgments and beliefs.
Many misunderstandings have accumulated around the cost of web applications and websites. We wrote separate articles about this, which we invite you to read.
We don't want to participate in such polemics; we prefer a calm and rational approach. Based on years of experience and knowledge of various markets.
Do you want to find out how much it costs to create a mobile application and what factors influence its final cost?
Is there a difference between Android app development and iOS app development?
You can find the answers here. Read on!
What is the cost of a mobile application? Introductory remarks
The popular industry answer to this question is: it depends. While no one likes this answer — including us — it's the answer that is both the least opinionated and the most honest.
Indeed, valuations and cost estimates are conditioned.
Of course, by browsing the Internet, we'll find more specific estimates. Under the popular search query – How much does a mobile app cost in 2024? — we will find the following app development cost breakdown:
- The cost of a mobile application with minimal complexity (MVP – Minimum Viable Product) is between $10,000 and $60,000
- A mobile application of moderate complexity costs between $60,000 and $150,000
- A mobile application of high complexity has a cost that exceeds $300,000
Mobile application is an extensive, ambiguous term; as a result, it takes work to determine the cost of its creation.
While the above division is reasonably accurate, it can nevertheless be misleading, if only because of its low specificity and generality.
It seems more useful to divide them by the application type.
Eight types of mobile applications:
- Basic applications (e.g., audio/video players)
- Data-driven applications (e.g., stock market apps)
- Authenticator applications (e.g., loyalty apps)
- Social media applications (e.g., Instagram)
- E-Commerce applications (e.g., Shopify)
- On-demand applications (e.g., Uber)
- Marketplace applications (e.g., Booking)
- IoT applications (e.g., smart homes)
Each of these types is a separate set of opportunities, necessities, conditions, and challenges.
It's also a separate collection of business, market, legal, technological, and user experience issues.
Without going into the details of a given mobile app development project, we're stuck with estimates. However, we must assume they'll be severely underestimated rather than close to the final amount.
What are the other factors that influence the cost of a mobile app?
The criterion of application complexity is popular and helpful in estimating the cost of mobile applications. However, it's not the only one.
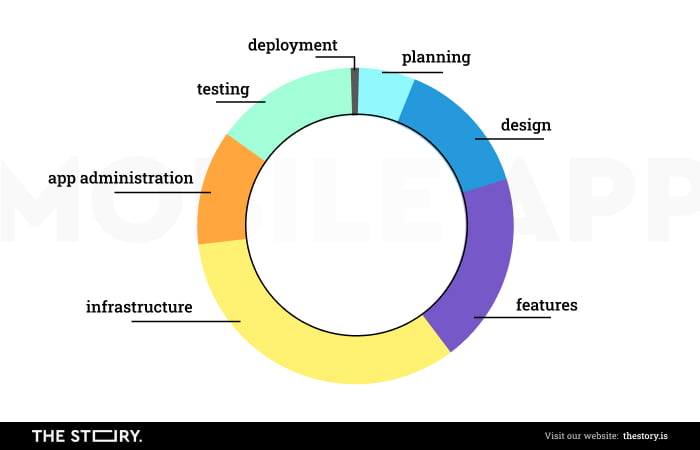
It's important to remember that creating mobile apps is a process. It's rather complex, lengthy, and has distinct stages.
The most fundamental phases of app development include the following:
- Pre-development
- Creation of a functional requirements list for a mobile application
- Design of application architecture
- Creation of an application prototype (also in terms of UX and UI)
- Front-end and back-end development
- Testing
- Eliminating errors, making corrections
- Publication on a specific platform
- Support and maintenance
All this work requires time and the involvement of various specialists, generating app development costs.
No mobile application can be developed without a complete, competent, and experienced team of specialists, which usually consists of the following:
- A business analyst (who researches business needs and designs the logic behind the mobile application)
- UI/UX designers (who, among other things, create application interfaces)
- Software engineers, front end and back end
- Quality assurance specialists (responsible for checking the operation of an application)
- Project managers/project leaders (responsible for the timely and smooth progress of the project)
- A system administrator
Of course, the number of representatives of a given specialization depends on the type of application, its complexity, the specificity of business goals, and the final deadline for its execution.
And this either lowers or raises the price. Also, the hourly rate for different specializations will vary significantly.
The architecture of a typical mobile application
Understanding the relationship between an application's complexity and cost requires an awareness of its design, components, and nature and the cost of these elements.
The architecture of a mobile application also has problems with its typicality and standardization.
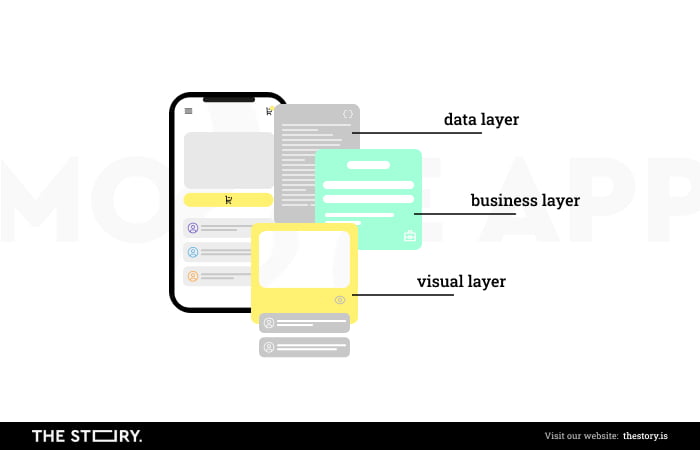
So the more the app has to be unusual, custom-made, and meet very sophisticated business and usability needs, the more its cost will rise.
In general, mobile application services can be divided into four categories:
- Functional services (e.g., push notifications)
- Infrastructural services (e.g., hosting)
- Administrative services (e.g., user management)
- IT support services (e.g., updates)
Third-party systems offer typical functional services (e.g., push notifications) and involve a paid subscription.
The mobile application cost can vary significantly depending on which provider is chosen.
This is because it involves not only the price of the annual subscription but also the level and complexity of the integration itself.
Infrastructural services refer to where and how applications are hosted, how data (including backups) is stored and secured, and how it's delivered.
Again, the choice of provider and how the application is integrated influences the cost.
Support and application maintenance aren't often included in the application's cost. This is a big mistake because choosing an application provider after its publication can cause many financial surprises.
Remember that every mobile application uses multiple external APIs, and any update of an external API requires checking and adjusting their cooperation.
Planning for such occurrences and including them in the cost estimate makes it possible to plan the mobile app development costs rationally.
Mobile app maintenance usually involves the following:
- Ongoing repair of errors that occur
- Technological updating of an application (counteracting the phenomenon of technical debt)
- Code optimization to make an app more stable
- Rescaling the server infrastructure as the number of app users grows
- User experience optimization
It's also worth remembering that design and technology decisions never have a short-term impact but long-term consequences that become apparent within days of a mobile app's release.
This is a costly relationship and something to be aware of.
How does the life cycle of a mobile app affect its cost?
A common mistake when budgeting for a mobile application is not considering the costs associated with its natural life cycle.
As mentioned in previous paragraphs, it includes its programming, implementation, and maintenance costs.
Every application generates profits, but it also creates costs, and they certainly don't end when the last line of code is written.
The proportions in programming, implementation, and maintenance costs will change over time.
Eventually, they'll reach a state opposite to the original one, which means that the cost of maintenance and development will be the highest.
That's why it's so important to correctly estimate future costs at the conceptual stage of an application's design.
The awareness of maintenance and development costs (mobile app development) and the possibility of optimizing them (e.g., with cheaper plug-ins) and several ready-made solutions (e.g., supporting application scalability) is necessary for:
- Accurate
- Reliable
- Exhaustive estimation, planning, and management of application costs.
Both present and future ones.
Mobile app development cost: Further factors
It's impossible to consider the cost of mobile applications without considering the relationship between their business goals, their usability, and the performance and accessibility they should provide.
The most difficult, time-consuming, labor-intensive, and costly issue in mobile app cost estimation is harmonizing business goals (business orientation, market orientation) and usability goals (user orientation).
Generally speaking, users appreciate mobile applications that are both attractive and useful.
Aesthetically pleasing design, ergonomic interface, attention to positive user experience, security, convenience, and ease of achieving goals and performing tasks are the requirements placed on applications by their typical users.
From a business perspective, a mobile application should provide an opportunity for stable growth.
Its development and maintenance should be as cheap as possible. In other words, it should be designed with short- and long-term business goals in mind.
The prospect of its growth (including unexpectedly dynamic growth, which can never be ruled out) should be indisputably included in its cost estimate.
The next variables considered in estimating the mobile app development costs are the following:
- Target platforms (Google Play and App Store, Android or iOS)
- Technologies (e.g., native app, hybrid app)
- App's functionalities and features (e.g., integrations with social media channels, maps, locations, task managers)
- Users (e.g., the ability to register, edit an account, method of logging in, push notifications)
- Integrations (e.g., camera, GPS, external APIs)
- Monetization (e.g., paid subscriptions)
- Maintenance and hosting
- Number of screens (e.g., profile screen, payments)
- Level of the complexity of the back-end layer
- Special effects and/or animations
As we can see, the cost of making a mobile app consists of very different factors. The primary factors that should be considered are its functionalities, business goals, usability, and range.
For example, the range is one of the dilemmas that influence the cost. It doesn't always make sense (in terms of business) to develop apps for all platforms (e.g., only for the Android platform).
Apple's iOS platform generally brings together fewer but more engaged users.
On the other hand, Google Android is seen as a much more popular platform; however, it attracts less engaged users who are more prone to uninstalling apps.
The choice of platform simultaneously means the choice of related mobile devices, which complicates application creation, maintenance, and development matters. Similarly, integrating an application with third-party systems is a strong cost-determining factor.
Native applications (those that meet the specifications of a particular operating system) are seen as more demanding in terms of design and technology, so their cost is higher.
Unfortunately, native apps, while providing a better match, require the creation of separate variants for each device. The challenge in their development is the need to use several programming languages.
Hybrid applications bypass the above problems and are considered as much less complicated.
If only because they're written in one programming language and are consequently easier to develop and maintain.
Unfortunately, they have a rather significant flaw. Their performance and scalability are significantly worse than those of native applications.
Looking at it from yet another perspective, the cost estimation of mobile apps depends on the following:
- The time required to produce it
- App developers
- The purpose of the app
The number of applications hasn't been closely related to their quality for some time now.
The increase in the number of new applications is so large that it's affecting the following:
- User loyalty
- User expectations
- Functionality, quality, and safety standards
This trend is forcing the direction of mobile application development. It enforces taking care of their higher competitiveness. It makes their creation more complex, challenging, and therefore expensive.
How much does it cost to create a mobile application? The cost of a UI/UX design
Mobile applications without research, usability testing, prototyping, task-oriented design, and a few other issues don't make sense today.
Simple, intuitive, ergonomic interface, navigation, attractive aesthetics, and security are mainly responsible for their success.
UX designers, UI designers, UX researchers, and UX writers simply can't be missing from design teams working on mobile app development.
Without understanding the typical and most common reasons for using mobile devices and applications, it's impossible to create a digital product that meets users' expectations.
Needs, preferences, and expectations are diagnosed and discovered by UX researchers using standardized, reliable, academically established research methods and techniques.
With the knowledge derived from research and testing, UI/UX designers can create solutions that address user needs much more accurately.
It's worth remembering that context dramatically affects how applications are used, received, and evaluated.
The situation in which they're used affects how smoothly they're operated, how focused our attention is on the task at hand, and how much we can engage in it cognitively and emotionally.
The crucial issue in designing an application is making it as easy as possible for a user to perform tasks.
It should be simplified as much as possible. Users' tolerance for mistakes should also be much higher.
Research, testing, and prototyping — necessary in developing a successful mobile application — also come at a high cost.
Reducing them is a shortcut that directly leads to market failure.
How much does it cost to develop a mobile application? The cost of security
The awareness of the risks of using mobile apps is growing among users. Combating them and offering applications that protect data, resources, and funds are now a standard and market necessity.
The financial expenditures on application security are growing and will continue to grow because an unprotected application is a commercial flop.
This is all the more obvious, the more the app's operation involves processing and storing critical data, such as health, finances, and personal data.
The issue of mobile application security isn't just about the security systems being implemented but refers to a whole class of problems related to diagnosing threats, neutralizing them, and predicting them.
Applying very standard security measures, such as encrypting sensitive data, authorizing user sessions, or implementing communication standards, involves a significant cost.
The more security we want to provide, the higher the cost we have to incur.
The impact of the billing model on the cost of a mobile app
Two billing models dominate the market — fixed price and time and material. Depending on the point of view (of whoever is looking and judging), they'll have different advantages and disadvantages.
There is no perfect method, in principle. If we want to create a mobile application, we'll always have to choose one of the options.
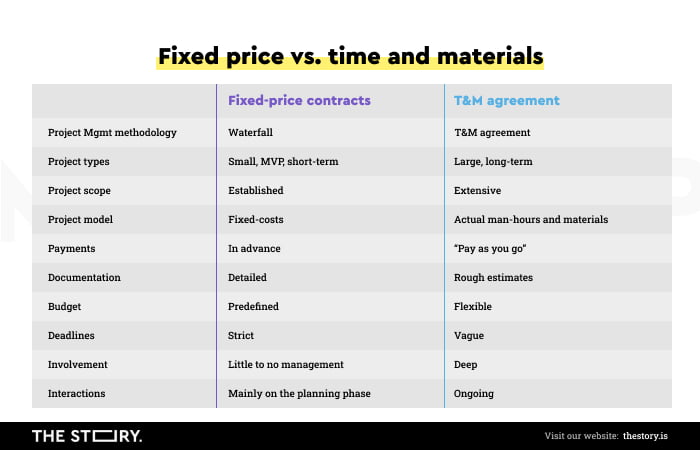
The fixed-price model is safer for the web development company customer because the cost is fixed and known in advance.
Fixed price works well in smaller projects, where it's much easier to define the scope of work and its schedule.
It's also easier to predict the project's development and possible problems. The direction of work in small projects is more clearly defined, and application development is more predictable.
However, everything has a price. The fixed price model is considered more expensive because the developer should include the risk of changes and delays resulting from the customer's decision-making process in the cost estimate.
For large projects, the time and material method is more appropriate and recommended.
The cost of the work is open, and payment is charged at an hourly rate. This method provides a lot more flexibility and is also considered less expensive, as developers don't have to worry about doing extra work without gratification.
Such a model is safer for the developer in projects where changes are inevitable, and the concept is more likely to be changed.
On the other hand, the client can still control the mobile app development budget and make the necessary changes to achieve a perfect mobile application.
How much does it cost to create a mobile application? Summary
- Mobile applications differ on at least a dozen dimensions, including price.
- The creation, development, and maintenance of applications have created many false beliefs and myths. At least a few fundamental issues differentiate the cost of developing an application.
- Evaluations and cost estimates of mobile applications (like web apps) are always conditioned.
- Mobile application is an extensive, ambiguous term; as a result, it takes work to determine the cost of its creation. Evaluating the cost of an app development project without specifying key variables will be, at best, an approximation.
- Each of the eight types of mobile applications presents a separate set of opportunities, necessities, conditions, and business, legal, technological, and user experience issues.
- The mobile app development process is complex and lengthy, with distinct stages.
- It's impossible to create a professional mobile application that has a chance to compete successfully on the market without a complete, competent, and experienced team of specialists.
- The scope and size of the development team depend on the type, complexity, and goals of the web development/app development company the application intends to fulfill.
- The hourly rate of each specialist varies significantly.
- Generally, a mobile application that meets very sophisticated business needs and exhibits better usability will be more expensive.
- Maintaining a mobile application usually means constantly repairing it, technologically updating it, and optimizing its code.
- Every application generates profits and, at the same time, creates costs. A mobile app's cost estimate should also consider balancing issues.
- Proportions in programming, implementation, and maintenance costs change over time.
- Over time, the cost of app maintenance and development becomes the most significant burden on an organization's budget.
- Predicting future costs as early as the conceptual stage is crucial.
- Awareness of maintenance and development costs and optimizing them are necessary for accurate, reliable application cost planning and management.
- When estimating the mobile app development costs, it's also essential to consider the target platforms, technologies, functionalities, users, integrations, maintenance and hosting, the level of complexity of the back-end layer, and special effects.
- Applications without research, usability testing, prototypes, and task-oriented design can't successfully compete in the market.
- The design teams must include UX and UI designers, researchers, and writers. The app development cost also depends on the number of required specialists.
- The financial expenditures on application security (the cost of maintaining a mobile application) will continue to grow, increasing the cost.
- Two billing models dominate the market — fixed price and time and material.
- Fixed price works well in smaller projects, where it's much easier to define the scope of work and its schedule. This model also significantly lowers the mobile app development cost.
- The time and material method is more appropriate and recommended for large projects. The cost of the mobile application is open, and the payment is charged at an hourly rate. This method provides a lot more flexibility.
Disclaimer
The sample prices presented in the article do not constitute a commercial offer within the meaning of the Polish Civil Code.