Today, it's not an exaggeration to say that Chatbots are used increasingly more often, and the future of Chatbots is more than promising.
We are entering the era of Chatbots. Bots are constant, integral elements not only in web applications but also in mobile applications.
Chatbots have also become much more financially obtainable.
They're an increasingly prominent element, a determinant of our experiences as users — they condition user experience (UX), and as customers — they condition customer experience (CX).
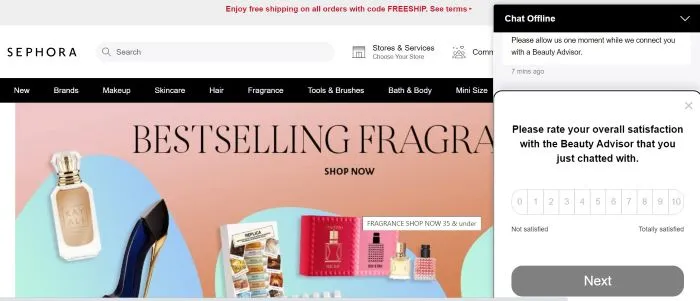
Chatbots, virtual assistants, and virtual advisors — are technologies most often associated with real-time customer service on websites.
They can be encountered in all conversational situations where customer satisfaction depends on how quickly the virtual assistant answers a question.
And the accuracy and adequacy of this answer — in short, it depends on the effectiveness with which the Chatbot can solve the problems of a user, customer.
However, it's only a part of the "truth" about these technologies. Chatbots, year after year, are used for increasingly diverse goals and appear in increasingly unobvious roles.
The way they're looked at is also changing. Having a conversation, communicating, and talking, thanks to the use of Natural Language Processing, Automatic Speech Recognition, and Natural Language Understanding, is for users increasingly less frustrating and is being met with more and more kindness and acceptance.
Trends prove in favor of technologies based on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning.
In general, in the near future, computer programs, or, to be more precise, artificial intelligence, will slowly reduce the need for new employees.
Communication through a Chatbot will be synonymous with customer service. Moreover, a computer program will be used for problem-solving, answering, and collecting information in a much more effective and versatile way than it is today.
Inevitably these trends are creating a growing conjuncture for creating even more perfect Chatbots. So, how should Chatbots be designed?
How to build a Chatbot? What are the stages and elements of this design process? What components, functions, and features does a professional, useful, efficient, liked-by-customers Chatbot need to have?
You will find answers to such questions in this article.
We cordially invite you to read on!
Chatbot — what is it?
Chatbot, Chatterbot, Linguabot, Bot, Talkbot, Interactive Agent, Artificial Conversation Entity — regardless of which name, label we prefer, we have in mind software that simulates natural human conversation through written text.
The answer to the question — What is a Chatbot? — is pretty simple. A Chatbot is a computer program used for customer service, ensuring improvement of work efficiency, based on artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Chatbots are based on artificial intelligence algorithms. They are programs that interact with customers in a way that is supposed to be as close in effects, feelings, impressions, and experiences as possible to human-human interactions.
During the early days of the development of this technology, Chatbots were built to work according to established guidelines which unfortunately made them very rigid and unnatural.
The current design trend is to base Chatbots on Machine Learning, thanks to which conversations are more natural and satisfying regarding effects and emotions accompanying human-machine interactions.
Chatbots appear in two basic variants, namely:
- Conversational Chatbots can use natural language to have conversations in which they don't only answer typical questions but also acquire data that allow them to learn.
- Rule-based Chatbots based on databases and prepared scenarios of questions, answers, and commands can provide answers.
Conversational Chatbots are created and developed thanks to machine learning, which means they are made based on artificial neural networks (which imitate the human brain's structure and way of functioning).
Such Bots are primarily focused on self-study — both at the lexical level (words) and more complex language structures.
In turn, Rule-based Chatbots are simpler and quicker to build and, thus, are much less expensive. However, their capabilities are significantly limited.
They don't use neural networks. Instead, they're based on rules created by a human in which the main problem, in addition to writing seamless, useful conversation scripts and dialogue scripts, is understanding the various intentions and how they're linguistically manifested.

Often Chatbots are used in industries in which contact with the customer and post-sale service are essential elements of the process.
Chatbots most often appear in the following industries:
- Telecommunications
- Shipping
- Logistics
- Finance
- Commerce (E-Commerce)
- Marketing
- Research
- Media and entertainment.
While designing Chatbots, you should primarily remember that an effective, friendly, and "human" Bot should provide users a value and benefit that they won't get in the case of traditional experience, interaction with a graphical user interface.
In other words, the conversation with a Bot must contribute more than just information that can be communicated with descriptions on dedicated pages, FAQ sections or infographics, and animations.
Most often, the added value is time — fast answers to questions — and usability, accuracy, and pragmatism of the answer.
What's even more important, a Chatbot is user-centered, especially in terms of their:
- Communication needs
- Goals (e.g., getting information, confirmation)
- Experiences (e.g., with Chatbots, Voicebots from similar industries)
- Expectations (e.g., regarding the speed and accuracy of working, flexibility of the dialogue)
- Conversation styles (e.g., formal, colloquial)
- Language competencies (e.g., regarding the used phraseology, lexis)
- Attitude toward language (e.g., its correctness, concreteness, distance, and style that is maintained, for example, through the use or omission of the form of address).
It's also crucial to precisely define the competencies and capabilities which the Chatbot has.
Advantages and limitations of Chatbots
The popularity of Chatbots didn't happen out of nowhere.
It's the result of their numerous advantages and relatively few drawbacks and limitations. The ratio of benefits to limitations and costs to profits is definitely favorable.
Above all, Chatbots are:
- Much more economical and have much more business sense than a traditional call center service — it's estimated that they can lower the costs of handling inquiries by up to 30% (Source: Chatbots Magazine)
- They aren't limited by working time or labor law — they continuously work 24/7 and 365 days a year
- More efficient, satisfactory, and effective
- More liked and appreciated for their convenience and provided quality of service
- Much more flawless and free from the typical human limitations of fatigue, overwork, health, emotional condition, speed of getting to crucial information, and tools
- Much more task-oriented, procedural, concrete, and goal-oriented, which can be measured and quantified
- Universal in terms of channels, devices, languages
- Useful for handling simple, typical, routine, repetitive questions, problems
- More helpful regarding data aggregation, analysis
- Much more useful in terms of filtering, categorizing, and addressing inquiries.
Besides purely functional, operational, and economic advantages, Chatbots bring additional benefits and profits to an organization.
Chatbots also provide benefits in the form of:
- Including them in the sales process, making them an important element of the sales funnel
- Incorporating them into the marketing process
- Increasing customer involvement, improving user and customer experience mainly through interactions aimed at probing needs, indicating solutions, giving shopping advice and suggestions based on previous user's activities
- Anticipating actions, and events (e.g., notifications about contract expiry)
- Using their potential in various channels (e.g., social media)
- Long and profound memory of preferences, actions, and choices of the user, thanks to which they show a better understanding of user/customer needs.
Chatbots can also have very diverse roles both "for" and "in" organizations as well as for their customers, business partners.
Often Chatbots supported by artificial intelligence have the following roles:
- Supporting problem-solving
- Advisory (virtual advisor, virtual assistant)
- Informative — which offers more than simply answers
- Helping — solving a problem
- Commercial, supporting the sales process
- Promotional
- Research — data aggregating
- Instructional
- Probing — of needs, expectations, and goals that are important for customer service
- Recommending
- Corrective — they acquire opinions and evaluations based on which it's possible to optimize processes and ways of service
- Adaptive in terms of language — they learn the language of the user/customer, and they can provide data that make it possible to better understand their needs
- Comparative — through learning cycles, they can correct their operation.
The authors of the article "Chatbot Design: Best Practices & 12 Insider Tips [2022]" add to the above list of roles and goals the following:
- Lead generation
- Reservation of meetings and presentations
- Answers to Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Rescue of abandoned shipping carts
- Opinion gathering.
Chatbots can also be used to promote the brand's values, especially when they simultaneously provide suitably satisfying interactions.
A lot of attention in analyses of Chatbots' potential is also being paid to the new customer service strategies that this technology can take to a new level.
Mainly thanks to the ability to aggregate and analyze data and thus customize the communication.
As with all technology, even Chatbots have their flaws.
Limitations of Chatbots include the following:
- Offering inadequate and irrelevant answers to the customer's problem
- Not understanding the user's problem
- Lack of empathy, ability to react emotionally, which relieves tension, frustrations
- Expensiveness — in the case of Chatbots handling complex processes and fulfilling various roles.
Chatbot Design
The starting point of Chatbot design should always be the end-user with their specific needs, expectations, experiences, and competencies.
Hence, it's important to use a well-defined, described User Persona, which should include the following:
- Age
- Gender
- Level and type of education
- Language competencies
- Technical skills
- Cultural capital.
The Persona allows you to answer the questions: Who is the end-user? And What does the end-user expect?
As well as What are the language capabilities of the end-user? What types of messages do they prefer?
And this is the key to designing the language, dialogs, conversations, goals, functions, and way of working of the Chatbot.
It's equally important to determine the following:
- Sets of typical questions
- Way of formulating questions
- Unmet needs behind the questions
- Actual issues related to the question.
During the designing process, paying special attention to questions about the Chatbot's functions, roles, and goals is also important.
Above else, you need to find answers to the following questions:
- What are the business needs of a company?
- How to make the Chatbot universal in a communicative sense so it can talk with various groups of customers?
- What questions, problems, expectations, and actions are typical, repetitive, and can be automatically handled by software?
- What area of the end-user experience is suitable for satisfactory automated service?
- What tone and language can be used for individual inquiries or problems?
- What will be the typical Chatbot use cases?
Equally crucial matters regard the following:
- Chatbot's goals — end-users need to know its scope of capabilities and operation
- Effects of the Chatbot — a change that will occur after talking with it (e.g., it can be obtaining information or taking action).
No less important is the way of communication with end-users. The Chatbot should use the following:
- Natural language
- Graphics, animations, images, icons, emojis, gifs, and avatars
- Interactive elements.
The optimization process of the Chatbot should be based on clear metrics such as:
- Customer Satisfaction — CSAT surveys (Customer Satisfaction Score) allow you to determine the level of customer satisfaction with the Bot's responses.
- Total Human Handover — an indicator of the total number of discussions that were handed over to human agents by the Bot.
- Completed Bot Conversations — an indicator of conversations that were entirely handled by the Bot and ended in a successful conversion.
It's also worth remembering that Chatbots can bring new value in a way that web or mobile applications can't achieve.
Moreover, Chatbots offer a different type of interaction than websites or mobile apps.
The primary difference in interaction with a Bot and an application is the difference in:
- Experience based on choice — web and mobile applications
- Experience based on a conversation — Chatbots, Voicebots.
A conversation is dynamic and doesn't boil down to selecting an element of the interface and clicking/tapping it. A conversation is a mutual exchange, and it develops over time.
Depending on the code of communication, speed of reactions, and way of reacting, it can take a very different course, and it can be a much less "mechanical" interaction with a graphical user interface.
The character of these interactions can't be underestimated or omitted.
One of the interaction elements is the ability to arouse emotions and react to them.
One way to evoke emotions is through surprise, which can be achieved by giving the impression of the Bot's intelligence, adding lightness and humor to its speech, and, above all, giving it "the ability to empathize."
Another essential element of the end-user interaction with the Bot is the time which should be filled with dialog aimed at a goal/task. With that said, occasionally, it takes time to achieve goals (e.g., to get to the information).
The waiting time should be filled in a particular way because the lack of Bot activity is often seen as a malfunction or incapability.
Hence, Chatbots should maintain the conversation with fun facts and news regarding services or digital products.
Finally, it's also worth remembering that Chatbots still evoke mixed emotions.
As Ruben Babu very aptly pointed out in the article "Designing an A.I. Chatbot: how conversational design changed the way I think about design" by writing that:
- Humans still haven't emotionally tamed artificial intelligence
- Artificial intelligence in some users causes mild trepidation
- AI creates distance, reinforces distrust, and intensifies suspicion
- Convincing people to talk with the Bot is challenging
- Gaining trust in the machine is a goal that should be as important as its effectiveness in solving users' problems.
Chatbot's user interface and UX writing
Designing a user interface for a Chatbot and UX writing are huge and complex subjects, definitely worth discussing in separate articles.
In the following paragraphs, we only signal the most critical issues related to appearance, the way the interface works, and the rules for formulating messages to Chatbot users.
You can't forget that design, interface design, and user experience significantly affect the Chatbot's reception and evaluation.
Chatbot's interface should have the following:
- Convincing, emotionally charged welcome screen
- Animations
- Suggestions
- Elements that enable gaining feedback
- Hints indicating desirable action — writing vs. clicking.
When designing the Chatbot in terms of language, you should remember that language in which the Bot communicates with the user needs to be efficient, inspire trust and summarize the terms on which the conversation is taking place.
The user needs to be certain of what they can ask and how they should formulate questions to obtain a satisfactory answer.
It's worth remembering that the conversation won't have a linear course (especially in the case of conversational Chatbots); it will be multithreaded and chaotic. Hence the Bot needs to skilfully react to an unclear message.
Suggestions and hints offered by the Bot are crucial.
Chatbot — what is it? Chatbot Design. Summary
- Chatbots are constant and integral elements of web and mobile applications.
- Chatbot is a computer program based on artificial intelligence that uses machine learning and is often used for customer service to improve efficiency.
- Chatbots interact with customers in a way that is supposed to be as close in effects, feelings, impressions, and experiences as possible to human-human interactions.
- The current design trend for Chatbots is to base them on Machine Learning.
- Machine Learning and neural networks make the conversations with a Chatbot more natural and satisfactory regarding the effects and emotions accompanying human-machine interactions.
- A conversation with a Bot — supported by artificial intelligence — should bring added value to the user's life, and it can't be boiled down to information that can be communicated on dedicated pages.
- Most often, the added value is time — fast answers to questions — and usability, accuracy, and pragmatism of the answer.
- Chatbots can also have very diverse roles both "for" and "in" organizations as well as for their customers, business partners.
- The starting point of Chatbot design should always be the end-user with their specific needs, expectations, experiences, and competencies.
- During the designing process, paying special attention to questions about the Chatbot's functions, roles, and goals is important.
- Chatbots offer a different type of interaction than websites or mobile apps.
- The primary difference in the interaction with a Bot and an application is the difference in the experience based on choice and experience based on conversation.
- It's worth remembering that despite the widespread use of Chatbots, they still evoke mixed emotions — users still haven't emotionally tamed artificial intelligence.
- AI stirs mild trepidation, distance, distrust, and suspicion.
- The design, interface design, and user experience significantly affect the Chatbot's reception and evaluation.