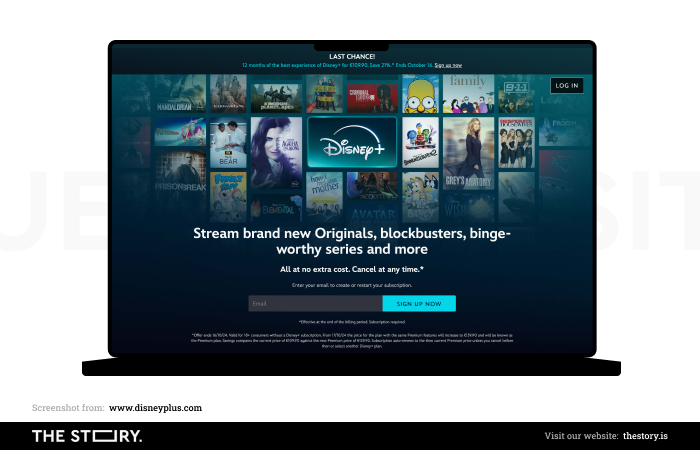
We covered the topic of value proposition in two articles: "Value Proposition. Examples of benefits" and "Value Proposition Canvas."
Now is the time to describe and explain USP (Unique Selling Proposition), often confused with Unique Value Proposition.
Although quite similar, the two propositions differ significantly and serve different purposes. How are they different? What exactly are they used for? Where and how to use them?
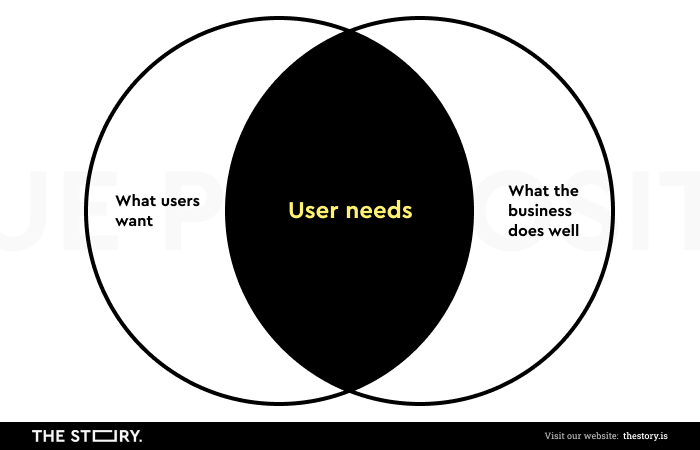
What is the character of the Unique Selling Proposition and Unique Value Proposition? Can they be used interchangeably or in conjunction?
Are the Unique Value Proposition and Unique Selling Proposition important for creating, positioning, enhancing, and offering digital products and making them more competitive?
These are the key questions to be asked and answered when discussing USP and UVP.
Announcing more comprehensive answers, we can simply say that without a solid USP, Unique Selling Proposition, and UVP, Unique Value Proposition, it is really difficult to win the market race and attract new users, subscribers, and customers.
These are the key elements of a successfully competing digital product, easily forgotten or considered a bit of a dispensable addition. As you might guess, it is a serious mistake.
Now then, if we have aroused your curiosity, enjoy the reading!
What does USP mean?
USP is an acronym for Unique Selling Proposition.
USP, or Unique Selling Proposition, is most often defined as a statement or a sentence used to communicate to the customers how they will benefit if they decide to buy a digital product or service.
Unique Selling Proposition should, first of all, be:
- Simple
- Concise
- Short
- Comprehensible
- Specific
- Unambiguous
- Distinguishable from the competitors' USPs.
Furthermore, Unique Selling Proposition should directly communicate to the customers how the product or service can meet their needs and how it makes your company stand out.
And how it will be the best answer to those needs.

And what is equally important and should be remembered when creating a USP is what distinguishes the offer from competitive offers.
When creating a Unique Selling Proposition, you should select one feature perceived by the Target Group (target market) as a real and unique benefit and characteristic only to this and practically no other product in a given segment.
A strong, relevant, and appropriate USP (Unique Selling Proposition) first and foremost results in action, motivates customers to purchase, and is persuasive.
In addition, you can recognize a good, accurate, and effective USP by how easily it deals with the most typical features that are powerful motivators, e.g., price.
What is a product USP?
Product USP, i.e., the product's unique selling proposition, is a statement or sentence referring to a specific product.
It refers to the most important from the customer's perspective feature of a given product, which makes it:
- More attractive
- More desirable
- More usable
- More functional
- Beneficial
- Effective
- Prestigious
- Reliable
- Guaranteeing the meeting of the customer's needs.
For example, and we will discuss USP examples in greater detail below, the USP of M&M's reads: "Melts in your mouth, not in your hand."
The brand's product USP emphasizes, above all, two features, values, and benefits: pleasure and convenience, that are perfectly combined in this product, which is to say that no other product can offer such a combination.
M&M's USP makes an apparent reference to common knowledge, experience, and problems of the consumers of chocolates.
Indeed, chocolate sweets very often melt in a very problematic manner under the influence of various heat sources (e.g., hand or sunlight).
M&M's will not surprise their consumers with such an undesirable effect that always occurs at the least expected moment.
What does a USP look like?
Unique Selling Proposition (sometimes also called Unique Selling Point) most often takes the form of a single sentence, but there are also more elaborate USPs.
An excellent example of a two-sentence USP is the unique selling proposition by Nike, which reads:
"Bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete in the world. If you have a body, you are an athlete."
Such a multi-dimensional and multi-faceted approach to creating USP is nothing special. All the more that a USP should include five essential elements.
The key components of every Unique Selling Proposition are:
- Evoking Emotions
- Indicating Benefits
- Defining Key Difference
- Highlighting Key Selling Points
- Competitive Advantage.
Naturally, it is not always possible, and sometimes even not desirable, to include all these elements in one sentence, especially if it is to be concise and sound suggestively, convincingly, and vividly.
As a rule, remember that emotions are evoked by the features that attract attention and are naturally and effortlessly perceived as advantages.
If a product is the least expensive, it is a feature that is attractive in itself. You don't need to convince anyone that a lower price is a sought-for and desirable value.
A Key Selling Point specifies what makes a given product superior to similar products.
A key difference indicates and defines the differences and distinguishes the product from the competition.
Competitive Advantage refers to the achievements, experience, and solutions that determine the uniqueness of a given company in a particular field.
There are at least a dozen ways to express differences, indicate advantages, and determine position and rank.
Commonly used words to communicate these features are the following:
- New
- Exceptional
- Enhanced
- Advanced
- Better
- Free
- Cheaper
- Proven
- Tailored.
Knowing what Unique Selling Proposition is and its components, we can move on to the examples of USPs cited as worth following and standing out from other USPs.
Examples of Unique Selling Propositions
In his article "21 Unique Selling Proposition Examples (and Why they Work)," Gareth Hancock points out three key features that a Unique Selling Proposition must have to influence customers effectively.
Unique Selling Proposition must be:
- Memorable
- Tangible
- Customer-Focused.
USP's memorability is achievable when the USP evokes strong emotions and is distinct from competitive USPs in form, content, message, and reasoning.
A real and tangible USP is a USP that is credible and results from what a company does, what it has achieved, what it is famous for, and what it can actually and undeniably offer and guarantee.
USP cannot be misrepresented and exaggerated or indicate non-existent differences that cannot be indisputably proved.
USP is a message that refers to the customer's needs and indicates the features and attributes of a digital product that are relevant and desirable to the customer.
Unique Selling Proposition: examples
Domino's Pizza: "You get fresh, hot pizza delivered to your door in 30 minutes or less—or it's free."
Anyone who got a pizza much, much too late (and almost cold) knows it is a fair approach.
The company challenges itself and makes an offer to the customer that is difficult to ignore. Whatever happens, the customer wins: either they get a pizza fast or free.
Avis: "We're number two. We try harder."
Avis's USP shows that even a potentially disadvantageous feature can be turned into an advantage by indicating consequences.
The second position on the market is obviously no reason to be ashamed, but it doesn't allow you to enjoy total success either.
From the customer's perspective, second place can be advantageous because it is clearly motivating.
Robinhood: "Investing for everyone."
The name obliges. Therefore, the USP goes very well with it, especially since the Robinhood investment platform is characterized by maximum inclusiveness.
The minimum investment threshold is 1 dollar. In this case, although USP employs an overused marketing word, "everyone," it expresses actual and tangible product characteristics.
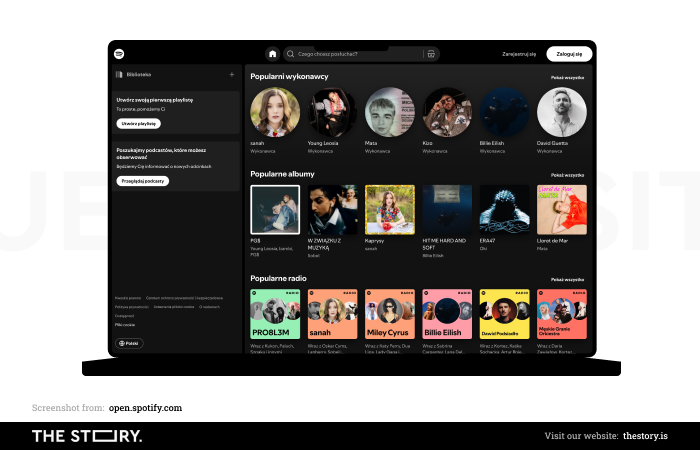
Spotify: "Listen without limits."
Spotify makes it possible to listen to music anywhere and anytime, keeping true to its value proposition.
What is a Unique Value Proposition?
Value Proposition, or Unique Value Proposition, is very often identified with Unique Selling Proposition, which, of course, is a mistake.
The likely sources of this confusion are the following:
- Linguistic nature of both messages
- Short form of a sentence or tagline
- Talking to the customer in the language of benefits
- Indicating, defining, and expressing the difference and uniqueness
- Simplicity and suggestiveness by principle.
Both statements and messages differ in several key issues:
- UVP is universal, refers to values, and uses reasoning that does not have to be as specific as in the case of USP
- USP serves to indicate a reason for purchase and motivates to purchase
- UVP addresses the need or problem and is a declaration of its fulfillment
- USP is sales-oriented and more immediate, while UVP is focused on a long-term effect and refers to a long-term perspective.
To put it slightly differently, Value Proposition (Unique Value Proposition) is a message informing the customer what a company can contribute to their consumer life and how and with what content and value it can fill it. It's also a tool that can help you capture customer loyalty.
For example, the USP of a specific model of shoes will try to convince the customer through quality.
For example: Only we give you a 5-year guarantee of quality!
While UVP will refer to something more immaterial but relevant, e.g., pride or a sense of belonging.
For example: Only professionals wear our shoes!
We discussed how to create a strong value proposition and examples of it in the article "Value Proposition. Examples of benefits." We do not want to repeat ourselves, so we encourage you to read it.
UVP in digital products. What are its characteristics?
Actually, you need to think about the tasks and goals a digital product enables the user to achieve.
How it works and what type of User Experience it provides. With digital products, not only the effects but also the roads that lead to them are important.
How a product works is as important, and sometimes even more important, as the results of its operation.
USP and UVP of a digital product more and more often communicate user experience and its uniqueness compared to the competition.
You cannot lose sight of the fact that a digital product is more than just a tool or a set of functionalities.
Although used to achieve goals in the first place, digital products are also popular, likable, valued, desirable, and used because of their added value expressed in a distinct Value Proposition.
And it is the Unique Value Proposition that allows you to rank and rate digital products and see clear and significant differences between products A and B and services X and Y.
UVP: how to determine product value?
There are at least a few ways to define and explore genuine product value (from the customer's and not the digital business owner's perspective).
The first step should be a thorough understanding and definition of the target group, the target audience, which should then be studied.
All guesses, suppositions, speculations, and conceptions are strongly discouraged.
USP and Value Proposition should be discovered and defined using exploratory research, which we discussed in more detail in the article "Exploratory research."
In the next step, you have to define exactly what type of problem the digital product or service solves.
When you know what you really offer, you can specify, organize and prioritize the benefits the customers and users are able to achieve.
Defining the benefits, values, differences, and promises enables you to understand the relationships between them. And this, in turn, inspires you to express them in the form of a clear, straightforward, catchy, and tangible sentence.
Unique Selling Proposition vs. Unique Value Proposition. Summary
- USP, or Unique Selling Proposition, is a statement or a slogan used to communicate to customers how they will benefit if they decide to buy a digital product or service.
- UVP, or Unique Value Proposition, is a statement informing the customer what a company can contribute to their consumer life and how and with what content and value it can fill it.
- Value Proposition, or Unique Value Proposition, is very often identified with Unique Selling Proposition.
- Unique Selling Proposition directly communicates to the customers how the product or service is able to meet their needs.
- When creating your own Unique Selling Proposition, you should select one feature perceived by the target group as a real and unique benefit.
- Key components of every Unique Selling Proposition are: evoking emotions, indicating benefits, defining key differences, and highlighting key selling points and competitive advantages.
- When creating a Unique Selling Proposition, first of all, remember its role, function, and form.
- Unique Value Propositions (e.g., with the use of Value Proposition Canvas) allow you to rank and rate digital products and see clear and significant differences between products A and B and services X and Y.
- Many Unique Selling Propositions and Unique Value Propositions (if not all of them) are used in marketing materials and marketing messages.