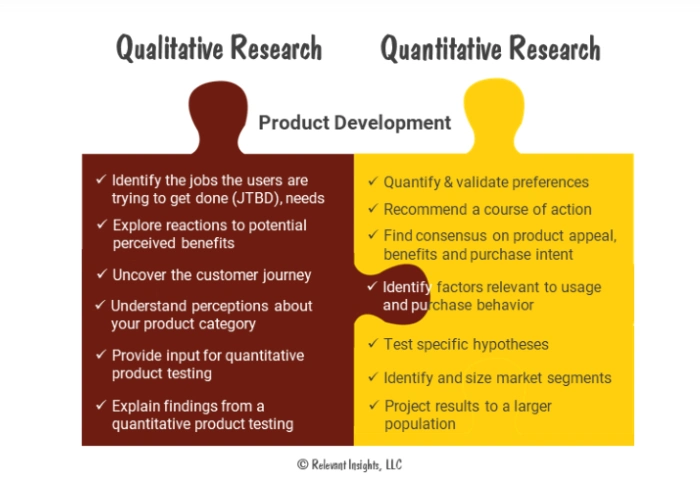
Quantitative and Qualitative Research is integral to the design and optimization processes.
Evidence-Based UX without UX Research, including Qualitative Research, cannot be done.
And very rightly so, because research provides a solid foundation that makes all the difference in designing and developing applications.
User Experience Research and Usability Research (Qualitative Research and Quantitative Research) are the basis for every stage of discovering, creating, developing, and optimizing a digital product.
They are one of the most rational and credible pillars of decision-making.
They help us avoid errors that come from subjective and personal preferences, prejudices, experiences, and limitations.
Qualitative Research is important in design, development, and business processes. Its role, functions, and benefits cannot be exaggerated.
At the same time, it is worth remembering that it is also not advisable to favor one type of research over another – qualitative over quantitative and vice versa.
The supremacy of one over the other is very artificial. Especially since, in the actual process of creating a digital product, both types of research are treated as complementary and equally necessary.
What do they involve? How to conduct Qualitative Research? What role does it play? How to analyze Qualitative Research?
How does Qualitative Research differ from Quantitative Research in User Experience? When talking about Qualitative Research, what methods are we thinking of?
How to design Qualitative Research? How much does their performance cost? How does the choice of research method affect the quality of the research?
These are the issues we will discuss today, and we will look for the best, most concise, and most illustrative answers.
We invite you to read on!
Qualitative Research – what is it?
Qualitative Research has its origins in the social sciences, such as anthropology, psychology, and ethnography. And on their grounds, methods for conducting it were developed.
The most concise answer to questions – What is Qualitative Research? What does it involve? How to describe it? – is to say that the clue of this research is to find an answer to the question – Why?
We should note that studies regarding User Experience fall into one of two main domains – Qualitative Research and Quantitative Research.
Qualitative Research is used to gain insight into the specifics of problems that users may be experiencing when using a digital product.
It involves, among other things, analysis of a given phenomenon (e.g., In-Depth Personal Interviews) and provides a more detailed understanding of the phenomenon under study, which is quite the opposite of what happens in Quantitative Research.
In a statistical analysis, such conclusions will not be possible.
It serves to provide a deep understanding of diverse user experiences. It is focused primarily on understanding user motivations and behavior.
Where Quantitative methods can only answer questions – Where is the problem? How many users are affected? – Qualitative methods more accurately explain what the problem is.

And above all, they allow us to understand how this problem affects users. In some cases, Qualitative Research supports the search for solutions.
In his book "Designing Qualitative Research," Uwe Flick defines Qualitative Research as studies that use text instead of numbers as empirical material.
Qualitative Research focuses on the viewpoints of research participants and their daily practices.
Qualitative Research consists of a set of interpretive, material practices. Qualitative researchers study items in their natural environment, trying to make sense of or interpret phenomena using the terms used by the people being surveyed.
A very interesting addition to the above definition is the description of the specifics of Qualitative Research presented in John W. Creswell's book "Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches."
When thinking about how to conduct Qualitative Research, Creswell notes that this kind of research:
- Takes place in a natural setting.
- Differs from Quantitative Research in that it does not form a priori hypotheses.
- Is unique because of the fact that a researcher is a research tool, the impact of which must always be considered and minimized.
- Allows us to obtain descriptive data, expressed not in numbers but in linguistic, discursive, and narrative forms.
- Focuses on the perceptions, observations, and experiences of its participants.
- Addresses processes and their consequences.
- Seeks the most complete, in-depth understanding of the phenomenon under study.
- Is idiographic – Data is interpreted on a case-by-case basis.
- Aims to reconstruct the reality of the respondents – How they perceive the world and how they function in it.
- Is open to exploration through intuition, feeling, and empathy.
- Increases its credibility, reliability of data, and results through consistency, insight, and instrumental utility.
Qualitative Research tries to provide the most reliable, honest, and unbiased answer that explains the causes, reasons, and mechanisms.
The key framework for Qualitative Research consists of the following:
- Conditions in which a study is conducted.
- Actors – respondents taking part in the research.
- Events – behavior and actions of the respondents.
- Processes – sequences of events.
- Ethical issues – specific approach to the study and respondents to ensure well-being and comfort.
- Strategies for collecting data – methods, techniques, and tools for collecting and classifying data.
- Data analysis procedures – methods of data interpretation.
In a general sense, Qualitative Research provides us with knowledge about:
- Needs
- Necessities
- Limitations
- Goals
- Obstacles
- Expectations
- Experiences
All these issues, more or less, directly relate to questions about causes and reasons.
Qualitative Research allows us to:
- Diagnose problems
- Determine the scope of a problem
- Understand relationships and mechanisms
- Recognize the structure and complexity of a problem
- Understand the necessity
- Discover hierarchies
In a pure design sense related to UI/UX Design, Qualitative Research allows us to:
- Create user-centered products
- Rationalize project, business, and technological decisions
- Build strategies
- Guide the development of digital products
What is Qualitative Research? Above all, it is a tool for discovering:
- What is simultaneously subjective and repetitive
- Motivation and goals
- Attitudes and emotional reactions
- Cognitive patterns
- Cognitive and behavioral limitations
- Functional, contextual, technological, and usual causes of errors.
When looking at the usefulness of Qualitative Research and how it relates to Quantitative Research, it is important to notice that it makes it possible to pinpoint a cause, to provide an explanation for quantitative data that only records frequency.
By adding the results of Qualitative Research and Quantitative Research, we will discover the following:
- How often a given event occurs (what is its intensity, dynamics, and distribution of changes over time)
- Why the event occurs (what causes it).
To put it differently, Qualitative Research of users of digital products (such as mobile applications, web apps, and software) helps to explain quantitative data.
For example, from a 25% Bounce Rate, we will learn nothing more than that 25 users out of every 100 will leave our site.
Why will they leave it? Why do users behave like that?
We will be able to discover this only by conducting Qualitative Research, which is used to find out causes and diagnose cause-and-effect relationships.
What Qualitative Research is not?
It certainly is not a universal remedy for all usability problems. It has its evident advantages as well as limitations and downsides.
The results are not a universal and stable truth. They are influenced by time, changes in the market and technology, needs, expectations, and users' behavior.
It is worth remembering a remark made in an article on Qualitative Research published on the website Naukowiec.org according to which Quantitative Research is not representative.
This means that we cannot use the results of this research for generalization. They cannot be used universally or in different, unrelated contexts.
They are not representative of users as such, but they are binding and relevant for narrowly defined groups.
For example, suppose we are studying an application interface for booking tourist trips. In that case, we cannot use the results of this study to design applications for diagnosing skin lesions.
However, this does not mean that Qualitative Research is entirely subjective.
Qualitative Research should aspire to objectivity through the researcher's reflective approach to their biases, preferences, and expectations.
Impartiality is a significant value that every researcher should consciously strive to achieve.
Confronting the results and interpretations of Qualitative Research with other researchers, thus programmatically making them more objective through intersubjective practices, also increases their credibility. And above all, it rips off the subjectivity patch.
Another way of dealing with subjectivism is carefully selecting a research method that fits the subject of UX research.
The tool that we will use is vital and cannot be random or chosen based on less important criteria – such as speed of study execution or its cost.
This approach always means a loss of quality and a decrease in the credibility and usefulness of obtained results.
When do we apply Qualitative Research?
In Qualitative Research, small groups – consisting of a handful to a dozen people – are usually studied. Its execution time is also generally shorter compared to Quantitative Research.

The digital product design process typically includes four phases: discovery, concept, creation, and validation. The use of Qualitative Research is recommended at each of these stages.
At every stage, research makes the design process more:
- Rational
- Predictable
- Specific
- Unbiased
- Clear
- User-centered
- Economical – By discovering usability problems at early stages, we can save the time and money necessary to make changes and eliminate errors.
The usefulness of Qualitative Research becomes most evident when there is an information deficit or the subject of the research is known to a small extent and which other research methods are unable to capture.
The exploratory nature of Qualitative Research makes it possible to discover new contexts, problems, ways of behaving, reacting, motivations, assumptions – their occurrence.
It helps diagnose, establish, and discover previously unknown connections.
Qualitative research – which involves, among other things, analysis – also allows us to expand our knowledge and reach a new conclusion.
Add new information to the existing ones – for example, more detailed information that uncovers new contexts of use related to products.
Qualitative Research is perfectly in sync with the iterative development process of web and mobile applications.
It is also priceless for monitoring changes in user behavior and expectations resulting from market, technological, business, cultural, and social changes.
Let's remember that the needs of users of digital products are changing very rapidly and dynamically.
In the world of digital products, several years is a period that stretches decades in other domains of the social world. Quantitative Research can capture these changes but cannot determine their nature, cause, logic, or purpose.
It is worth remembering the dual nature of Qualitative Research. It is simultaneously:
- Formative – It supports the decision-making process
- Summarizing – It supports the process of evaluation and validation of effects.
With its help, it is possible to continuously develop the digital product and make it "Relentlessly Up-to-Date."
Where do we apply Qualitative Research?
In research, design, and optimization practices, Qualitative Research is recommended at every stage of digital product development.
In particular, Qualitative Research will be useful when:
- It is necessary to make (design) decisions that bind and determine the future of a digital product.
- It is necessary to identify already existing and potential usability problems.
- A digital product is conceptualized, created, optimized, and developed.
User Experience Research and Usability Testing of digital products are crucial for:
- Product competitiveness
- Satisfaction and loyalty of users
- Strategic product development
- The dynamics of growth in market share.
Qualitative research finds application in those situations, contexts, and problems where it is necessary to obtain relatively quick and inexpensive as well as relevant feedback.
It is recommended wherever a rational approach to the design or optimization process is necessary.
Where User-Centered Design is not just an empty phrase but is a value that allows us to create digital products focused on the needs and expectations of the end user.
What are the benefits of conducting Qualitative Research?
The benefits of using Qualitative Research Methods will differ slightly in each project.
Nevertheless, at the most general level, Qualitative Research is, first and foremost:
- Relatively easy to conduct.
- Accessible in terms of organization, budget, and time.
- Optimal in regard to the quality/cost ratio.
- Informative – It helps to understand and thus offers more relevant and adequate solutions.
- Illustrative – It makes it easier to present research results to stakeholders. They are more accessible and communicative.
While writing about the benefits, we cannot forget to mention the limitations of Qualitative Research.
The most frequently mentioned drawbacks of Qualitative Research are:
- Lower credibility of the results compared to the results of Quantitative Research (according to the principle stating that numbers cannot be argued with).
- Lower validity of the obtained results, which may be caused by an insufficient number of respondents or incorrectly defined criteria for including respondents in the study.
- Higher dependence of the result on a researcher's experience, knowledge, competence, attitude, and professional ethics.
- The prejudice of some stakeholders regarding data that cannot be quantified and presented in the form of clear bar charts.
Qualitative Research Methods
Among the most popular Qualitative Methods used for User Experience Research are the following:
- Interviews, in which a UX researcher discusses a problem with respondents in a one-on-one format.
- Field research, in which UX researchers conduct a study with users in their natural environment, in which they use a digital product.
- Focus groups, in which a UX researcher interviews several respondents simultaneously.
- Moderated/Unmoderated Usability Tests, in which respondents perform tasks defined by a researcher.
- Card sorting, which examines the mental models of app users.
User interviews – one of the most popular research methods – provide a deeper, broader, more precise understanding of users' needs, motivations, and behaviors.
Field research allows us to understand typical ways of using applications and explore how context determines how a digital product is used and evaluated.
Focus groups provide a significant amount of qualitative data characterized by diversity, representing different perspectives, experiences, needs, and expectations.
How to conduct Qualitative Research?
The quality of Qualitative Research is crucial, as it is what ensures high credibility, usefulness, and reliability of the research.
Only very meticulous enforcement of the procedures and methodologies established in academic fields makes it possible to conduct Qualitative Research characterized by high quality.
Qualitative Research should be carried out:
- With a method that is adequate and allows us to achieve the purpose of the study as well as possible.
- With respondents who have been recruited according to the accepted criteria for recruiting respondents.
- Without feeling pressured by time or budget and without having to make unfavorable – from the perspective of reliability of results – concessions.
- In conditions and locations that do not affect how people think, act, and use the digital product, the research context should be as natural as possible.
- In a way that should minimize the influence of a researcher on the attitudes, behavior, reactions, and emotions of respondents.
- With a focus on discovery, not confirmation, that is why open questions that do not impose or suggest answers should dominate.
- Without stress, the pressure of time, or result.
Qualitative Research in UX. Summary
- Quantitative and Qualitative Research is integral to designing, optimizing, and developing processes.
- Qualitative Research is essential at every stage of discovering, creating, developing, and optimizing a digital product.
- They help us avoid errors that come from subjective and personal preferences, prejudices, experiences, and limitations.
- It is not advisable to favor Qualitative Research over Quantitative Research and vice versa.
- Qualitative research is used to gain insight into the specifics of problems associated with using a digital product (e.g., a website).
- Qualitative Research tries to provide the most reliable, honest, and unbiased answer that explains the causes, reasons, and mechanisms.
- It allows us to discover the cause and provide an explanation for quantitative data that register only the frequency.
- We should not treat Qualitative Research as a universal remedy for all problems with usability.
- The results are not a universal and stable truth. They are influenced by time, changes in the market and technology, needs, expectations, and users' behavior.
- The exploratory nature of Qualitative Research makes it possible to discover new contexts, problems, ways of behaving, and reacting and find previously unknown connections.
- Qualitative Research is also used to monitor changes that occur in user behavior and expectations.
- Only very meticulous enforcement of the procedures and methodologies established in academic fields makes it possible to conduct Qualitative Research (of a website, for example) characterized by high quality.