What do sales of digital products, digital content, online courses, online stores, products solving a particular problem, and ebooks have in common?
They're all digital products.
In our articles, we often use the term "digital products," leaving its meaning, scope, and definition implicit.
The concept of digital products (e.g., digital file sales) seems intuitive enough, but is it?
Today, we'll examine issues related to digital products, discuss their specific nature, characteristics, and categorization, and answer the question: What is a digital product?
According to the Digital Transformation Market Size Report, the global digital transformation market was estimated at 880.28 billion dollars in 2023.
This means that digital products are on offense today. The digitization of business processes expands its scope each year, and this trend will continue for a long time.
Digital products increasingly function as alternatives to traditional products or services (e.g., online shopping vs. brick-and-mortar shopping). In many cases, they have successfully replaced their offline analogs.
When talking about digital products, you can't forget about their user experience.
The digital revolution is also a revolution in awareness of the user experience's role, function, and benefits.
UX is increasingly essential for websites, mobile applications, software, games, and digital services.
And rightly so, because this means we'll live in a much more user-friendly world where usability will be an important quality criterion.
As the term "digital product" becomes increasingly synonymous with the word "product," it's imperative to tailor it to the user's needs and expectations.
Digital products: meaning and characteristics
Digital products are products and services (frequently provided in the form of SaaS, software as a service) whose distinctive feature is their intangible nature. You can sell digital products on various platforms, such as websites, e-commerce stores, and online marketplaces.
Digital products don't have a physical form, but they're sometimes sold on physical media.
However, digital products are often offered as digital files and accounts purchased online on various platforms (e.g., an online store, social media, etc.).
Digital products offer users specific functionalities based on a clear benefit-sharing relationship.
The intangible nature of digital products and the different methods of their offering, distribution, use, sales, and ownership give rise to several issues:
- Legal
- Logistic
- Technological
- Commercial
- Business
- Cultural
- Market
- Ecological
Online business and digital products also have their specifics expressed in a completely different lifecycle and new customer expectations.
The method of creating, placing on the market, developing, optimizing, growing, maturing, and going down in history is quite different from that of traditional material products.
It requires expertise that wasn't needed for the preparation of material products. A distinct nature also characterizes digital products.
The digitization of products and services also influences the digital business transformation covered in our article "Digital Business Transformation." The contemporary business landscape differs significantly from the scenery from half a century ago.
An excellent example of this change is the presence of Bill Gates and Jeff Bezos, digital business owners, in the top ten of the wealthiest people in the world. The article "WTF is 'Digital Product'?" by Jules Ehrhardt sheds a slightly different light on digital products, indicating deeper and deeper penetration of digital products into our daily activities.
The presence of digital products is so prevalent and concerns such diverse devices as computers, phones, watches, TVs, fridges, and cars that it's necessary to introduce the concept of digital touchpoints.
Digital products increasingly function not only as applications with mouse- or touch-controlled interfaces but are offered as a kind of conversation (e.g., Amazon Echo).
The interaction effect also changes.
Digital products provide information and enable users to perform tasks and achieve goals. They aren't only tools but are increasingly becoming partners with the users.
Digital products — examples and key features
Digital products are intangible goods sold and made available in digital format.
What are digital products? Examples of digital products' categories:
- Digital media: radio stations, TV channels, streaming platforms
- Digital applications: web, mobile, and desktop apps
- Educational platforms: online courses
- Digital product sales platforms: Shopify, Udemy
- Service platforms: HubSpot, Zendesk
- Gaming platforms: Steam, GOG
- Social media platforms: Facebook, Instagram
- Digital articles: ebooks, digital files
- Digital means of exchange: cryptocurrencies, tokens
- Digital identities: e-IDs
- Digital subscriptions: newspaper subscriptions
- Digital tools: Zoom, Trello, Mailchimp

Apart from their intangible nature, the common features of digital products are:
- Scalability
- Universal access: no time and spatial limitations, which is the essence of digital product sales and which has been and still is limiting the sales of traditional products
- Very good cost-to-profit ratio
- The capability of more straightforward automation of multiple business, organizational, and frontend and backend processes
- Flexibility
- Multi-channel offering: digital products usually function in several distribution, information, and communication channels.
In his article "Digital Goods and the New Economy," Danny Quah adds a few more characteristics to complete the picture.
According to him, digital products, or digital goods, are:
- Nonrival
- Infinitely expansible
- Discrete
- Aspatial
- Recombinant
Goods are nonrival when their use by one user doesn't compromise their usability for other entities.
An online product is infinitely expansible, as any quantity can be "manufactured" fast and without extra costs.
A digital product is discrete because it always functions as a copy. Digital goods are aspatial, as they're both everywhere and nowhere at the same time.
Digital products are recombinant, meaning they're cumulative and formed by a combination of components before the new variant.
All these qualities make them extremely attractive for businesses and desirable for customers, which is as much a symbiotic combination as it is opulent. A digital product enables you to make a much higher profit quickly and at a much lower investment cost.
Digital products have the potential to offer the possibility of obtaining much more for much less, mainly due to their scalability.
Creation of digital products — a competitive digital product
Digital products, e.g., in the freemium version (you can find more about business models of digital products in the final section of this article), must always constitute a value for the users and must respond to their needs.
They must provide a desirable type of experience, high usability, and be characterized by added value, making them irreplaceable for a long time and unbeatable in the eyes of a given user.
To that effect, you must create digital products that are:
- Customer-oriented
- Consistent
- Concise
- Measurable
- Compatible
- Cool
- Contextual/customized
A good digital product solves one unique problem in a very attractive way for its target audience.
By the way, the most influential design trend currently is user-oriented design, which is focused on users' needs, abilities, and experiences.
We covered this issue in more detail in the article "Human-centered design vs. User-centered design."
A good digital product is consistent, meaning that its experience is the same regardless of the channel (e.g., introducing a product to desktop and mobile online stores must involve the same benefits).
A web and mobile application should offer the same type of experience and provide the same results, capabilities, sensations, and satisfaction.
A good digital product is concise. Therefore, its operation, communication, and problem-solving should be as simple, fast, and attractive as possible.
A good digital product is measurable, so its features, functions, and results must be quantifiable.
A good digital product is compatible when the best design patterns and recommendations have been used in its design, creation, and development, ensuring a very positive user experience and high usability.
A good digital product is cool when it is attractive and keeps the promises made in the value proposition.
It's aesthetically pleasing and creative and evokes strong positive emotions, e.g., strong attachment.
A good digital product is contextual if it enables the user to adapt its mode of operation to individual needs in real time and predicts future preferences based on a set of predictors, e.g., behavior, preferences, transaction history, and location.
Furthermore, some authors complement the above list with additional features and attributes that a digital product must have.
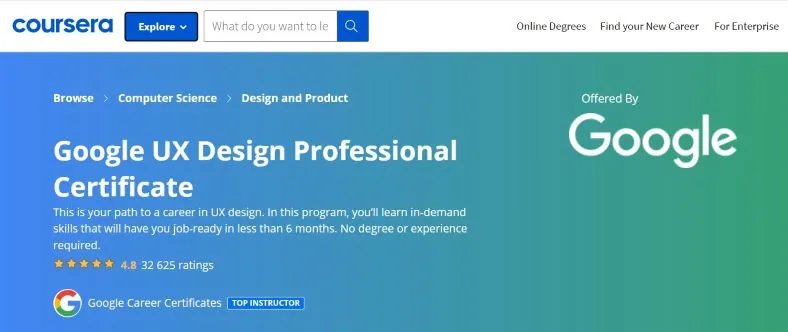
According to general expectations, good digital products must also be characterized by the following:
- Usability
- Utility
- Reliability
- Efficiency
- Desirability
A good digital product is usable when it's understandable, easy to learn, and adapted to the user's language.
A good digital product is useful when it fulfills the customer's needs through innovative technology.
A good digital product is reliable when it's free of fatal flaws and offers long-term, stable, and trouble-free use.
A good digital product is effective when it enables the users to achieve their goals quickly and efficiently, considering the conditions and limitations of a typical user context.
A good digital product is desirable when it's aesthetically pleasing, emotion-evoking, and creative.
All the above features constitute constellations of interconnected characteristics that determine one another.
Without utility, we can't talk about real, satisfactory usability. In turn, without usability, no product will be perceived as attractive. If a digital product is unattractive, it can't provide a superior and desirable user experience.
Selling digital products: benefits
We talked enough about what digital products are, but what benefits can selling them online bring?
Flexibility
Since digital products lack physical form and are sold online, you don't need to worry about keeping an eye on inventory or worrying about shipping and delivery methods. Moreover, digital products allow you to make your products better and better. They aren't just finished and done; they can keep evolving.
High profit margins
Another benefit of digital products is that you can sell them constantly without little to no additional costs. The number of copies you can sell is unlimited, and because you eliminate the costs of restocking, maintaining storage, and delivery, you can earn more. In theory, you can sell online in perpetuity.
Efficiency
You don't have to waste time on logistic issues like delivery or packaging. This saves you time and money and allows you to deliver products to your customers immediately.
Scalability
The size and complexity of your digital product aren't the only things that can grow. As you develop your business, your sales can increase from a few units to hundreds. The advantage of digital products is that they facilitate this jump in growth because you don't need to worry about logistics. The only things you can improve are the capabilities of your selling platform to handle more traffic and the availability of customer service.
Selling digital products: examples of digital product ideas
Here we present some ideas that can help inspire you to create your own digital products:
- Digital art
- Software
- Applications
- Photos
- Ebooks
- Online courses
- Guides
- Digital templates
- Music
- Website themes
Digital product lifecycle
The specific nature of digital products, distinguishing them from the offline world, is their continuous change in time.
Subsequent versions (e.g., WhatsApp version 2.22.11.82) not only indicate a digital product's current status but also suggest its past and announce its future.
Digital products are not just static products. The changes introduced in them are continuous and regular.
Moreover, the introduced changes' scope, nature, and results aren't always directly visible to the users (e.g., because they don't use specific functionality or use it too rarely to notice the change process).
Metaphorically speaking, a digital product is always a work in progress. The digital product creation process doesn't even assume achieving an ultimate goal or the final shape, the definitive form.
Digital products constantly evolve because they must maintain adequate sensitivity, flexibility, responsiveness, and adaptability to the changing market, business, technological, and social or cultural conditions.
However, this doesn't mean they aren't subject to laws and don't function in a cycle. As with any product, digital products also go through certain phases.
From the most standard perspective, a digital product goes through the following stages:
- First, it comes into existence with an idea, a concept that is expanded and complemented by a vision, motivation to develop a digital product, strategy, market, user research, budgeting, and the definition of a value proposition.
- Next, it enters the design and development phase, during which prototypes are created, the first studies are conducted, the first MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is developed, and usability tests are conducted.
- Then, a digital product enters the growth phase, in which it is confronted with assumptions, imperfections are discovered, and modifications are introduced.
- In the next phase, the maturity phase, we're dealing with maintaining the market position gained and with the need for continuous development, which allows us to update and adapt the product to changing expectations and needs, thereby protecting it against aging.
- In the downward phase, the product loses its appeal and market position and is unable to meet the new expectations.
Strategic digital product management requires awareness of its evolution and appropriate prediction, customer research, and measurement of changes, such as using proper metrics.
The goals of digital product evolution include the following:
- Raising brand awareness among customers
- Increasing the number of users, customers, and subscribers
- Extending brand and product loyalty (retention)
- Development, optimization, and improvement of functionalities
- Increasing usability and security
What are the types of digital products? Digital product business models
Of course, business models and methods for offering digital products are very diverse. They depend on business goals, the nature of the product itself, and customer and user habits and expectations.
E-commerce model
Of course, Amazon is the pioneer of this model. It has become synonymous with digital products, enabling sales and purchases online. Amazon is at a completely different point today. It was initially selling physical products and still does so, but its catalog of digital products is equally impressive.
Ecosystem model
Amazon, Alibaba, and Apple are examples of the most prominent digital ecosystems with transnational, global reach.
The core of this model is multiplying digital services and products that are more or less interconnected, which results in customer dependence on the provider.
The cost of leaving the ecosystem and resigning from services is so high, discouraging and exceeding the potential benefits, that users rarely decide to do so.
Experience model
In this model, the digital experience usually extends and complements the physical product customer experience. In many cases, it's the critical component without which it's impossible to use the physical product.
Free model (Ad-supported model)
The free model should, of course, be treated conventionally.
The essence of this model is to provide the users with a digital product without the need to pay for a subscription.
However, the price is to turn the user into the product being sold, whose value is expressed in the data generated and left in the form of a digital footprint.
The customers are simply products.
In the second variant of this model, the user must view advertisements to use an application free of charge.
Freemium model
Software companies have popularized this model by offering customers basic application functionalities for free.
More advanced functionalities are available for (regular or one-time) subscriptions.
Hidden revenue generation model
The hidden revenue generation model usually means earning revenue by charging license fees.
On-demand model
It's most commonly used in streaming platforms that offer digital content access (movies, podcasts, music, libraries). Customers pay for time-limited access to a selected item.
Open-source model
Due to its non-commercial nature, the open-source model can be questioned as a business model, but it is a model of offering, sharing, and distributing digital products.
Most open-source digital products are used and developed pro bono.
Subscription model
The subscription model involves purchasing time-limited access (usually a monthly or yearly subscription) to a product or service.
During access, the customers can use the full version of the product that is being updated. A subscription is usually offered monthly, semi-yearly, or yearly.
How to sell digital products online: step-by-step guide
What exactly can you do with the knowledge presented above? What does the process of selling digital products look like?
1. Look for ideas.
When looking to get inspired, the crucial thing is not to overthink your ideas. Write down everything that comes to mind. You will eventually sift the ideas when doing more in-depth research, and you can't do that if you don't have any.
You can look for potential ideas on online forums, social media, trade press, and various online articles.
2. Validate the chosen idea.
You need to validate your idea before you start creating and selling digital goods. During the validation stage, you ensure your product idea has potential. This can prevent you from starting a venture that will quickly fail.
You can research the potential of your idea using the following tools:
- Google Trends
- Keyword research
- Product reviews
- Industry forums
- Prototypes (cheap and small)
3. Find your target audience.
With your idea in hand, it's time to consider your target audience carefully. You need a specific target group so you can customize the product to the needs of its users. This will also help with designing your brand language and marketing strategy. Researching your potential customers will aid you in offering them the benefits and values they desire.
If you try to cater to everyone, your digital product is more likely to reach none.
4. Create your own website or e-commerce store.
Once you transform the validated ideas into products, you must create a website or e-commerce platform to sell digital products. You don't need a proprietary and dedicated website at the beginning of your journey. Numerous e-commerce platforms, digital marketplaces, and applications can help you start your online store.
You can choose from platforms such as Amazon, Shopify, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, Adobe Commerce, and PrestaShop.
Alternatively, you can commission a web development company to help you create an online store.
5. Optimize your platform and market your product.
Creating an online store to sell digital products is not the end of your journey. You still need to optimize it to generate organic traffic and drive sales. How to do that?
SEO optimization needs to become your new best friend. That's how you increase the organic traffic. To rank higher in search engines, you need to research relevant keywords, see what customers are looking for, and implement them on your site. You also should ensure that your store loads fast so users don't leave it prematurely.
To increase your marketing efforts, you can establish cooperation with influencers. This will help you reach a wider audience and promote your product. This can work in the form of affiliate programs when you work with a third party whose goal is to advertise your product in exchange for receiving a commission.
You can also try offering a lead magnet. This means offering a benefit to a customer in exchange for, for example, their contact information. It can be done in the form of signing up for a newsletter in exchange for receiving a free ebook or offering access to the digital product for free for a certain amount of time. These activities can help you build trust and reputation and consequentially turn into actual sales.
What are digital products? Summary.
- Digital products are becoming increasingly popular, and the digital business transformation expands its scope and gains importance.
- Digital products are products and services distinguished by their intangible nature.
- Digital products are offered as digital files or accounts purchased online on various platforms.
- Advantages of selling digital products include flexibility, efficiency, scalability, and high-profit margins.
- If you want to start selling digital products online, you can create an online course, make digital art, design a website theme, or build a digital tool.
- The lifecycle of digital products, including their creation, market implementation, development, and optimization, is entirely different from that of physical products.
- A digital product provides information, enables the user to perform tasks, serves as a tool, and increasingly becomes a partner to the user.
- A digital product enables you to earn much more at lower costs and in a very short time.
- Digital products must be customer-oriented, consistent, concise, measurable, compatible, desirable, and customized.
- A good digital product solves one unique problem in a very attractive way to its target audience.
- Without utility, you can't have real and satisfactory usability. And without usability, no product can be perceived as attractive. If a digital product is unattractive, it cannot provide an excellent impression and desirable user experience.
- The specific nature of digital products is their continuous change in time.
- The digital product creation process does not assume the development of its definitive version, shape, or form. The customers do not expect it either.






