What does the job of an IT Analyst in the IT industry entail? IT Business Analyst, IT Analyst acquires and analyzes perspectives, points of view, and needs and transforms the collected information into the requirements specification.
Furthermore, they help stakeholders see the difference between what they say and what they actually expect.
What else does an Analyst do?
An IT Business Analyst teaches, asks, listens to employees, organizes, and learns.
The final goal of their work is to develop, introduce changes, supervise, propose technology solutions for a particular project, and improve business processes.
The above definition of an IT Business Analyst is perhaps one of the most concise and illustrative. Although not 100% exhaustive, of course.
We can add that IT Business Analyst, IT Analyst is a profession, specialization, and role in teams that develop web applications, mobile apps, digital products, or software.
It's a job performed by people with technical (IT skills) and business competencies.
If you're curious about the requirements for IT Business Analysts, what is the scope of their responsibilities, tasks, work, and what competencies they need to have, then be sure to read this article.
The role of an IT Business Analyst in the software development process is crucial and fascinating. That's why today we'll tell you about it.
So, without further ado, we invite you to read the article!
What is Business Analysis?
In the trade press, in advertisements, job offers, IT Business Analyst is frequently called an application analyst, requirements analyst, requirements engineer, requirements manager, system analyst, or business system analyst.
Regardless of the adopted and preferred terminology, IT Business Analyst is mainly responsible for correct, exhaustive, and reliable diagnosis and collection of the following:
- Functional requirements (visible behavior of a system in various situations)
- Non-Functional Requirements (not really determining what the system does but how well it does it).
Their main objective is to identify the needs and determine what functionalities must be included in the software.
Correct, clear, and consistent with actual needs determination of functional requirements allows developers (programmers) to implement them successfully.
In theory, with this summary, it may sound simple and innocent. But is it?
In practice, it's much more demanding because misunderstanding and misreading the business needs and user requirements by the IT Business Analyst may result in implementing functionality that nobody will use.
Professional and successful digital transformation without the IT Business Analyst is challenging to imagine.
IT Business Analysts are responsible for adapting digital products to user requirements and the business objectives of stakeholders.
Tasks that Business Analysts face aren't easy. Often people who want to pursue the job of IT Business Analyst are expected to have various interdisciplinary competencies.
On the International Institute of Business Analysis website, in the article "What is Business Analysis?," Business Analysis is defined as actions aimed at determining the needs and recommending solutions that bring value to stakeholders.
In IT projects, in the software development process, the IT Business Analyst is primarily responsible for documenting functional requirements included in the Software Requirements Specification (SRS).
Requirements specification (functional specification) should, as exhaustively as possible, describe the behavior of the system under development (e.g., mobile application).
The specification is a crucial document and tool.
It's used by designers, programmers, testers, quality controllers, and people involved with project management.
It's essential to present the requirements specification in such a way that, through proper form, organization, and formatting, supports the understanding and prioritization.
The functional specification should reflect business needs as illustratively, comprehensively, accurately, and precisely as possible.
The goal of any Business Analyst should be to strive for the most communicative form possible. The clarity of requirements is the primary objective.
While creating the requirements specification, the IT Business Analyst cooperates with developers.
This cooperation aims to assess the feasibility of implementing each requirement in a digital product.
It's not just about purely technological capabilities but also timeframes, budget, and organization.
Confronting business needs with technical capabilities and limitations allows you to estimate chances, risks, and potential conflicts and, last but not least, see existing dependencies.
It enables you to estimate the project's or digital product's complexity — to determine the amount of time, work, and the extent of the required and necessary resources.
It also provides opportunities to look for simple, equivalent, less costly, or less risky solutions.
The structure of the development of requirements should include the following:
- Acquiring requirements
- Analyzing requirements
- Specifying requirements
- Validating requirements.
The requirements specification should also precisely determine the following:
- Goal and scope of the project
- Success criteria
- Business requirements
- Functional requirements
- Non-functional requirements
- Use cases
- Business rules
- User interface
- The course of processes
- And any other project-specific dependencies.
In summary, Software Requirements Specification determines functionalities and capabilities that a software system must execute and defines characteristics and limitations the system should consider.
SRS should:
- Describe the system's behavior in different conditions
- Determine the desired system's characteristics (e.g., efficiency, security, and usability)
- Be a fundament for planning, designing, and coding the project.
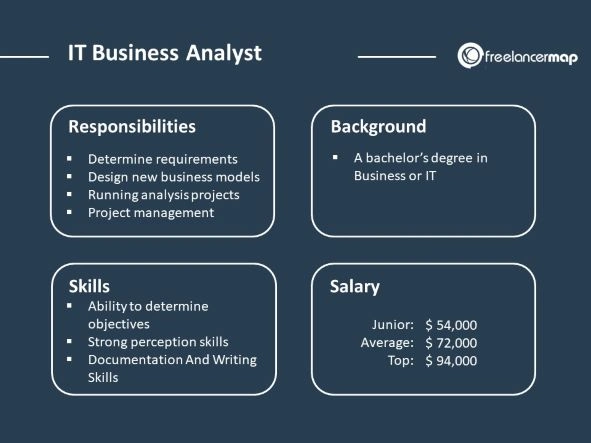
What tasks and role do the IT Business Analyst, IT Analyst has?
IT Business Analyst, IT Analyst, in a sense, is an interdisciplinary profession in which it's necessary to have various competencies.
IT Business Analysts need to have skills, competencies, and experience in the following:
- Economy, business, management
- Information technologies
- Data analysis
- Business process analysis
- Interpersonal communication
- Leading and managing projects
- Benchmarking
- Market analysis.
The IT Business Analyst is a mediator, interpreter, and middleman communicating business requirements from stakeholders to developer teams. They also analyze various data to inform business decisions.
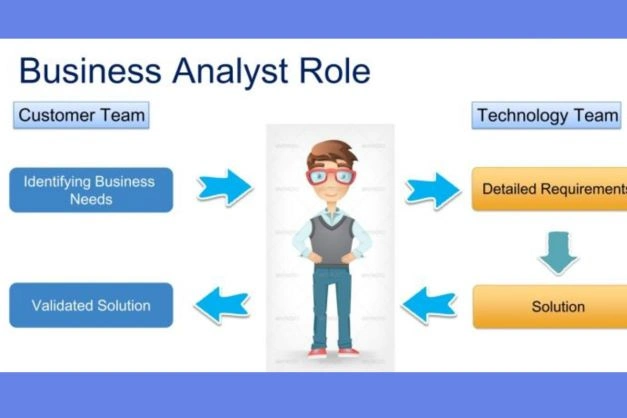
With that said, they aren't only responsible for the successful and complete forwarding of information essential to executing the project, but also they collect and maintain documentation of the product that is a fundament of its improvement and development.
Their daily activities and responsibilities include the following:
- Analysis of needs and business goals
- Analysis of processes
- Analysis of competitors
- Market analysis
- Collecting stakeholders' expectations
- Documenting requirements for the software
- Managing communication between stakeholders and project and development teams, as well as system architects
- Diagnosing and analyzing current processes and technologies
- Creating data models
- Creating user documentation.
Generally speaking, The Business Analyst role consists of improving processes and optimizing products, primarily through data analysis and business analytics.
Their task is to efficiently link the world of technology with the world of business.
They make data-driven recommendations using data analytics and provide solutions, reports, studies, business insights, and analyses that allow business stakeholders to make more accurate business and technological decisions.
Their role is to support business decisions, suggest the most optimal solutions, and plan, monitor, and report.
Prioritization of technical and functional requirements is another competency that professionals working as IT Business Analysts must possess.
Business Analyst, IT Analysts the scope of responsibilities
What is a Business Analyst? What does a Business Analyst do? What is the scope of the Business Analyst's responsibilities? What skills can be found in the business analyst job description?
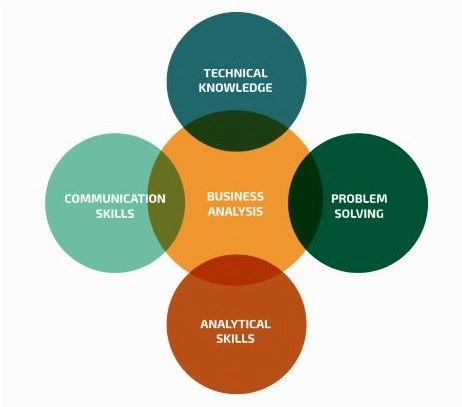
As we've mentioned, IT Business Analyst is a role in a team, a job requiring broad competencies — both soft and hard skills.
An effective IT Business Analyst must have the following:
- Above-average communicative skills
- Facilitation skills
- Interpersonal skills
- Technological knowledge
- Market, industry, and product knowledge
- Character and personality traits that strengthen social skills.
The Institute of Business Analysis expands expectations for the Information Systems Business Analyst position to include the following:
- Interpersonal skills (e.g., listening, talking, asking)
- Analytical skills
- Organizational (e.g., meticulousness, concreteness, reliability, inquisitiveness)
- Process modeling skills
- Fast decision-making skills
- Systems thinking.
In other words, a priority for IT Analysts is understanding the operations, conditions, mechanisms, and business goals and learning about its formal rules (e.g., legal framework) as well as informal ones.
Moreover, the Analyst position recruits professionals who can primarily think of the business as a collection, a sum of processes.
Also essential is the design of functions, their impact on the organization, its environment, customers, data analysis, and, last but not least, the ability to think logically.
What does a Business Analyst do in the software development process?
As we've said, the role of the IT Business Analyst is to collect business and technical requirements that are essential to creating prototypes or Minimum Value Products (MVPs).
But is this the only benefit of this specialist's work? As you might have easily guessed, no.
It's worth remembering that the quality of IT business analysis influences the following:
- End result — usability, functionality, attractiveness, and business adequacy of the software
- Reliability and flawlessness of the software
- Punctuality of project completion
- The final cost of the project
- Competitiveness of the software
- Optimization and development of the software
- Effectiveness of the business's digital transformation.
The role of the IT Business Analyst is especially significant in projects that are:
- Complex in terms of business logic, processes, and business goals
- Complex regarding technology
- Custom, unique, unusual
- With many limitations (e.g., legal, logistic).
In such projects, the Business Analyst fulfills a crucial role, meaning:
- Supportive
- Advisory
- Diagnostic
- Supervising
- Orchestrating.
They should be able to support decision-making and reinforce searching for optimization and alternative solutions related to the project's development.
It's worth remembering that software is never a finished product; it's always, more or less, work-in-progress.
Hence, business analysis is necessary at every stage of the digital product development cycle.
Business analysis is also very helpful at the product testing stage and quality assurance.
Functionality testing aimed at detecting errors and security vulnerabilities is also more effective when the IT Business Analyst is involved.
It's also advisable to keep in mind that in the projects led in agile methodologies (e.g., Scrum), Business Analysts are also responsible for the long-term, strategic vision of the product.
They can define the limitations of the project and indicate the direction of its development.
The Business Analyst in an agile project will be extremely useful for the following:
- Preparing detailed documentation of requirements
- Determining the best method for keeping the registry of requirements
- Strengthening the sense of having a common goal and priorities in all the teams involved.
We'll end the article with a little fun fact. Namely, according to the article "Business Analyst Career & Job Description," American cities such as Washington D.C., New York City, Chicago, Los Angeles, Sacramento, Boston, Seattle, Minneapolis, Atlanta, and Dallas have the largest number of business analyst jobs, and the average business analyst salary (as of May 2021) is $93,000.
IT Business Analyst — their role in the Software Development process. Summary
- IT Business Analyst acquires and analyzes perspectives, points of view, and needs.
- Moreover, the Business Analyst transforms the collected information into a requirements specification.
- The role of the Business Analyst is to help stakeholders see the difference between what they say and what they actually expect.
- IT Business Analyst is a profession, specialization, and role in teams creating web applications, mobile apps, digital products, and software performed by people with technical (IT) and business competencies and soft and hard skills.
- IT Business Analyst is primarily responsible for correct, exhaustive, reliable collection of functional requirements (visible behavior of the system in different situations) and non-functional requirements (determining not only what the system does but how well it does it).
- The main task of the UX Business Analyst is to identify the needs and determine what functionalities need to be included in the software.
- It's worth remembering that misunderstanding and misreading the business needs and user requirements by the IT Business Analyst can result in the implementation of functionality that doesn't meet the expectations of users and stakeholders.
- The IT Business Analyst is primarily responsible for documenting functional requirements included in the Software Requirements Specification (SRS).
- The requirements specification should, as exhaustively as possible, describe the behavior of the system under development.
- The specification is a crucial document and tool. It's used by programmers, testers, quality controllers, and people involved with project management.
- The functional specification should reflect business needs as illustratively, comprehensively, accurately, and precisely as possible.
- One of the most important goals of any Business Analyst should be to strive for the most communicative form of the created specification.
- The IT Business Analyst cooperates with programmers while creating the requirements specification.
- This cooperation aims to assess the feasibility of implementing each requirement in a digital product. It's not just about purely technological capabilities but also timeframes, budget, and organization.
- The structure of the requirements development process should include acquiring, analyzing, specifying, and validating requirements.
- Software Requirements Specification determines the functionalities and capabilities that a software system must perform.
- Requirements specification also defines the characteristics and imitations which the system should consider.
- Business analyst skills include competencies and experience in business administration, knowledge of information technologies, data analysis, interpersonal communication, experience in leading and managing projects, benchmarking, and market analysis.
- The IT Business Analyst is a mediator, interpreter, and middleman communicating business requirements from stakeholders to developer teams.
- IT Business Analysts recommend solutions and provide reports, studies, and analyses that allow business stakeholders to make more accurate business and technological decisions.
- The role of Analysts is to support business decisions, suggest the most optimal solutions, and plan, monitor, and report what helps streamline software development for companies.
- IT Business Analyst requires broad competencies — both soft and hard skills.






